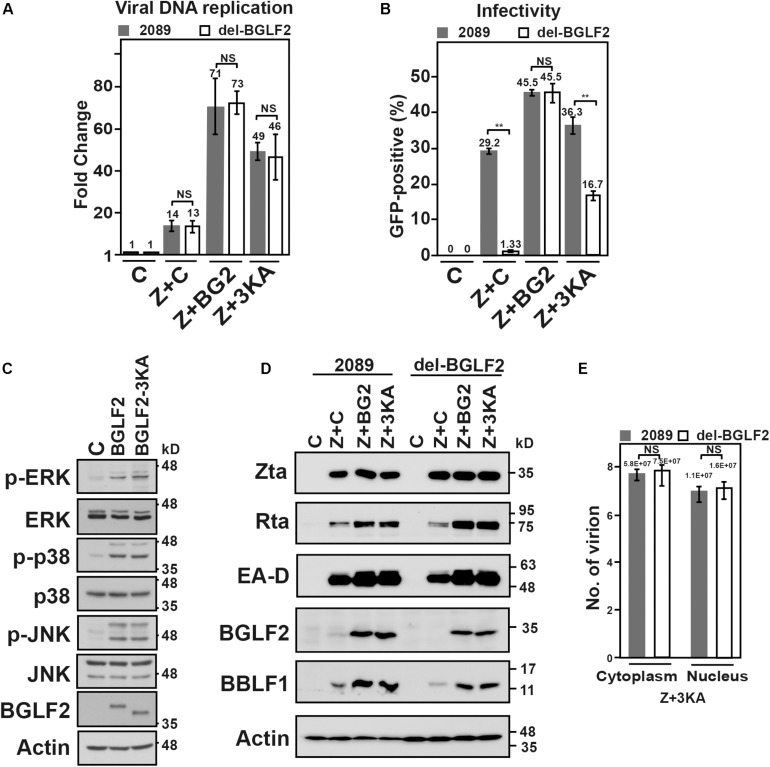
FIGURE 7.
Genetic complementation of the del-BGLF2 mutation. (A) HEK293 (p2089) and HEK293 (del-BGLF2) cells were cotransfected with pCMV-Zta and empty vector (Z + C) to induce the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) lytic cycle and also cotransfected with pCMV-Zta and BGLF2 (Z + BG2) or BGLF2-3KA (Z + 3KA). The amount of EBV DNA relative to that in the control cell lysate at 48 h after lytic induction was determined by qPCR using primers specific to EBNA1 gene, which was normalized against the number of copies of PIK3CA. (B) The culture media were used to infect Raji cells. On day 3 post-infection, the percentage of Raji cells that were GFP-positive was determined by FACS analysis. The experiments were conducted three times, and the results were analyzed statistically using the t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; NS, not statistically significant. (C) 293T cells transfected with pCMV3 or plasmids that expressed V5-BGLF2 or V5-BGLF2-3KA were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies 48 h post-transfection. (D) HEK293 (p2089) and HEK293 (del-BGLF2) cells were cotransfected with pCMV-Zta and empty vector (Z + C) to induce the EBV lytic cycle and also cotransfected with pCMV-Zta and BGLF2 (Z + BG2) or BGLF2-3KA (Z + 3KA). On day 3 post-transfection, proteins in the lysate were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Rta, anti-EA-D, anti-BGLF2, anti-BBLF1, and anti-actin antibodies. (E) HEK293 (2089) and HEK293 (del-BGLF2) that were cotransfected with pCMVZta and pCMV-BGLF2-3KA were lysed with 0.5% NP40 at 48 h post-transfection, and the lysate was then separated into cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. The samples were treated with DNase I and proteinase K. The encapsidated EBV DNA was purified and quantified by qPCR. NS, not statistically significant.