Figure 4.
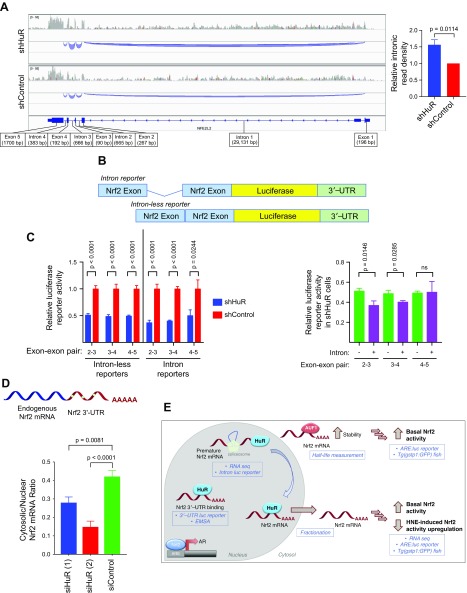
HuR knockdown suppresses Nrf2-mRNA splicing and nuclear export of Nrf2-mRNA. A) Integrative Genomics Viewer (71) view of splicing tracks for Nrf2 (NFE2L2) from RNA-seq analysis of shHuR and shControl HEK293T cells. The area of the blue tracks corresponds to the levels of intronic RNA detected. Shown is 1 representative replicate per cell line. Inset at right: areas of splicing tracks integrated with ImageJ (mean ± sem, n = 4 introns). See also Supplemental Fig. S11. B) Reporters to read out the effect of introns were constructed by fusing a portion of Nrf2-mRNA (with or without the intron) upstream of a firefly luciferase reporter. As with the 3′–UTR reporter (Fig. 3C), effects on this construct can be assayed by measuring luciferase activity in the lysates of cells expressing these reporters. C) Reporter levels upon HuR knockdown in nonstimulated HEK293T cells for both the intron-less reporter (left) and the intron reporter (right) (mean ± sem of n ≥ 7 per set). Inset at right: Comparison of reporter activity in shHuR cells (i.e., blue bars from the main plot in C upon introduction of introns. D) Real-time qPCR was used to measure the ratio of endogenous Nrf2-mRNA in nuclear and cytosolic extracts of HEK293T cells depleted of HuR [mean ± sem of n = 8 for siHuR (1, 2) and n = 7 for siControl]. E) Model of post-transcriptional regulation of Nrf2-mRNA by HuR and AUF1. HuR regulates Nrf2-mRNA maturation and nuclear export, and AUF1 stabilizes Nrf2-mRNA. Shown in blue text/boxes is the experimental evidence supporting each facet of this regulatory program. All P values were calculated with Student’s t test.