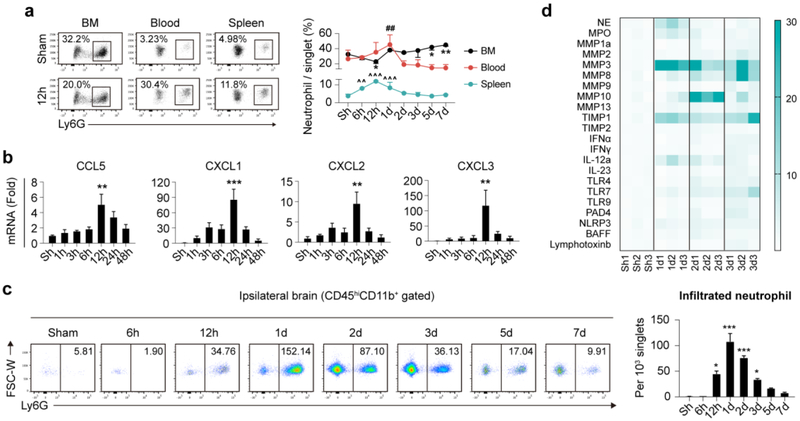
Fig. 2.
Temporal and spatial dynamics of neutrophil after ischemic stroke. Male C57/BL6 mice were subjected to 60min tMCAO and sacrificed at various time points. a Neutrophil constitution in bone marrow (BM) blood and spleen of mice as assessed with flow cytometry. N = 3-5. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, versus Sham in BM. ##P ≤ 0.01, versus Sham in blood. ^^ P ≤ 0.01, ^^^ P ≤ 0.001, versus Sham in spleen. b Expression dynamics of neutrophil attracting chemokines (mRNA level) after ischemic stroke. N = 3. **P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001, versus Sham (Sh). c Temporal dynamics of infiltrated neutrophil after ischemic stroke as assessed with flow cytometry. Number in the representative flow panel = neutrophil per 103 singlets in ischemic hemisphere. N = 3-5. *P ≤ 0.05, *** P ≤ 0.001, versus Sham (Sh). d Heat map showing expression dynamics of neutrophil related inflammatory mediators in ischemic hemisphere as analyzed with qPCR. N = 3. Statistic analysis was displayed in Fig. S2c. FSC, forward scatter; W, width; hi, high; NE, neutrophil elastase; MPO, myeloperoxidase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; TLR, toll-like receptor; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain-containing 3; PAD, peptidylarginine deiminase type; BAFF, B cell activating factor.