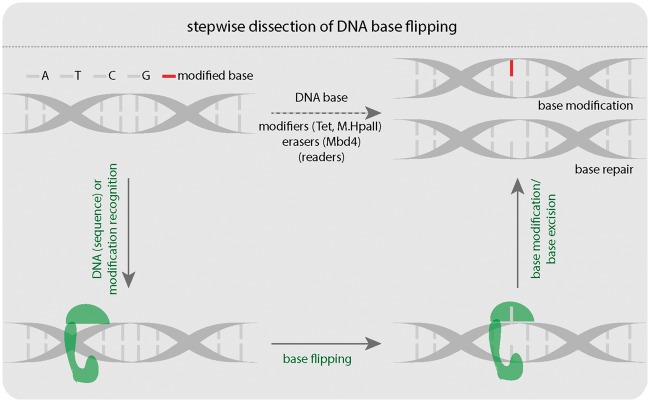
Figure 1:
Stepwise dissection of DNA base flipping. Three steps: (i) protein–DNA binding, (ii) base flipping, and (iii) base modification are involved in DNA base modification or repair. A: adenine, T: thymine, C: cytosine, G: guanine. Tet: Tet-eleven translocation protein. M.HpaII: HpaII methyltransferase. Mbd4: Methyl-CpG binding domain protein 4. The green shape represents protein, which binds, flips, and modifies DNA bases.