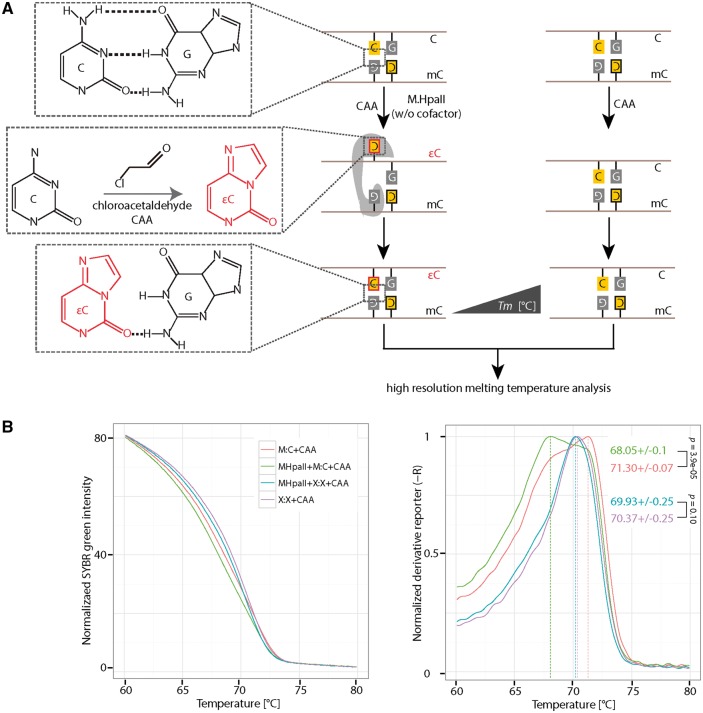
Figure 4:
Detection of HpaII methyltransferase (M.HpaII) mediated DNA base flipping. (A) 0.5 µM of hemimethylated or non-CCGG containing DNA was incubated with or without 1.25 pmol (4 units) of M.HpaII in the presence of 30 mM CAA. CAA reacts with cytosine when it is flipped out of the DNA helix. The reaction product 3,N4-ethenocytosine (εC) disrupts hydrogen bonds with the base guanine in the complementary strand. The presence of 3,N4-ethenocytosine (εC) can be detected with HRM analysis, due to its low Tm contribution to double-stranded DNA. (B) Normalized SYBR green fluorescence intensities (left) and the corresponding derivative of intensities (right) were plotted using RStudio. Independent experiments were repeated two times. Shown is one representative result with three technical replicates. The P-values of student’s t-test are indicated in the plot. Tm: melting temperature. C: cytosine; G: guanine; M:C: hemimethylated DNA; X:X: non-CpG containing DNA.