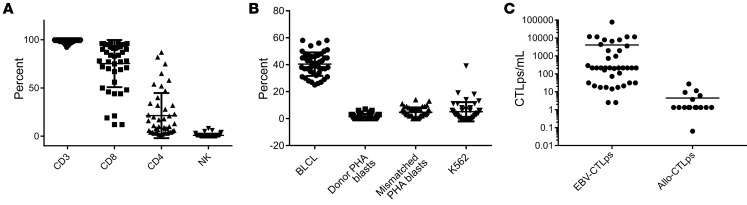
Figure 1. Characterization of 55 EBV-specific cytotoxic T cells infused.
All T cell lines, including those predominantly containing CD4+ T cells, demonstrated EBV-specific cytotoxic activity against autologous EBV-BLCLs and did not kill NK cell–sensitive targets (K562), EBV-negative autologous or recipient-derived PHA blasts, or HLA-mismatched EBV-BLCLs. (A) Phenotype (CD3, CD8, CD4, and NK). (B) Cytotoxic activity of EBV-specific T cell lines against autologous BLCLs (circles), autologous PHA blasts (squares), mismatched targets (triangles), and NK-sensitive K562 targets (inverted triangles). (C) EBV-CTLp frequency and alloreactive CTL precursor (allo-CTLp) frequency in lines infused to treat patients. In limiting dilution assays, the EBV-CTLs contained a median of 6323.5 EBV-CTLps per 106 cells (range, 2.5–76,982 EBV-CTLps per 106 cells), and, in response to irradiated fully allogeneic PBMCs, generated low or undetectable alloreactive CTLps (median 1.2, range 0–27.4 allo-CTLps per 106 cells). Error bars indicate ± SD.