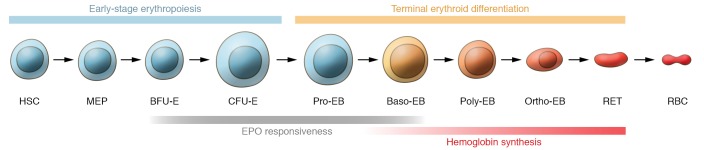
Figure 1. Erythroid differentiation pathway.
Pathway starting with an uncommitted hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) and leading to the first committed erythroid progenitor cell (burst-forming unit–erythroid, BFU-E). This marks the start of erythroblast proliferation followed by distinct phases of terminal erythroid differentiation to produce mature red blood cells (RBC). The pathway is depicted as linear for simplicity, but cellular proliferation at early stages amplifies red cell production. MEP, bipotent megakaryocytic-erythroid progenitor; CFU-E, colony-forming unit–erythroid; Pro-EB, proerythroblast; Baso-EB, basophilic erythroblast; Poly-EB, polychromatophilic erythroblast; Ortho-EB, orthochromatic erythroblast; RET, reticulocyte; EPO, erythropoietin. Adapted with permission from Nature Reviews Nephrology (56).