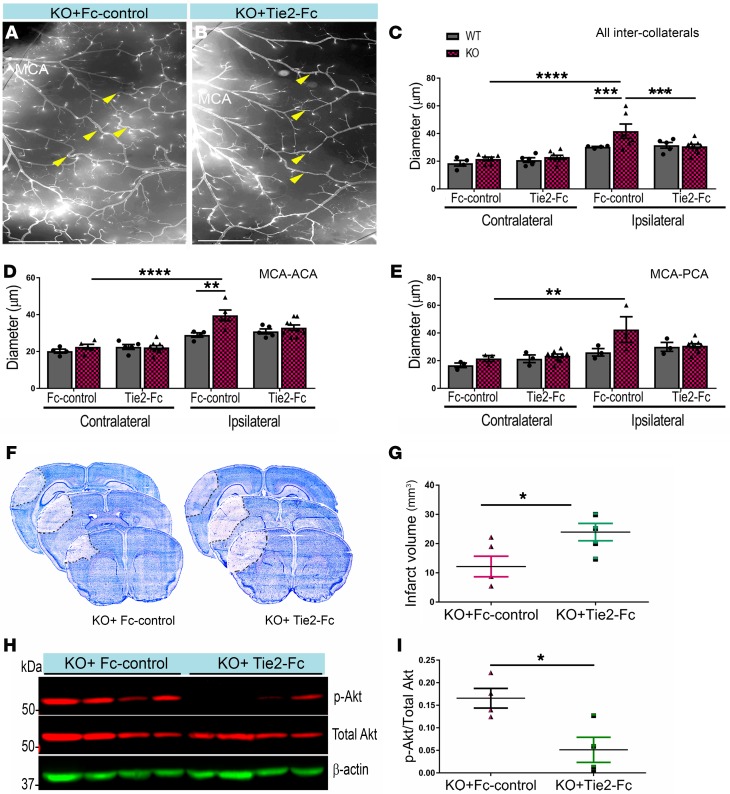
Figure 5. Blocking Tie2 receptor attenuates neuroprotection and p-Akt in EC-specific EphA4 KO mice.
(A and B) Ipsilateral hemisphere of vessel painted pMCAO KO mice after Fc or Tie2-Fc treatment. (C) Quantitative analysis shows a reduction in the diameter of total inter-collateral KO mice treated with Tie2-Fc compared with Fc-treated mice; n = 5–9. WT mice showed no significant difference following Tie2-Fc; n = 4–5. (D) MCA-ACA collateral diameters. (E) MCA-PCA collateral diameters. (F) Representative Nissl staining of Fc and Tie2-Fc brains 1 day after pMCAO, demarcating the area of infarct. (G) Quantified graph shows that Tie2-Fc–treated KO mice have a significant increase in infarct volume compared with Fc-treated KO mice. (H) Western blot analysis of ipsilateral brain lysates from Fc- and Tie2-Fc–treated KO mice 1 day after pMCAO. (I) Quantified graph shows that Tie2-Fc–treated KO mice have reduced p-Akt expression compared with Fc-treated mice; n = 4 mice per group. Unpaired t test and 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Scale bars: 1 mm (A and B).