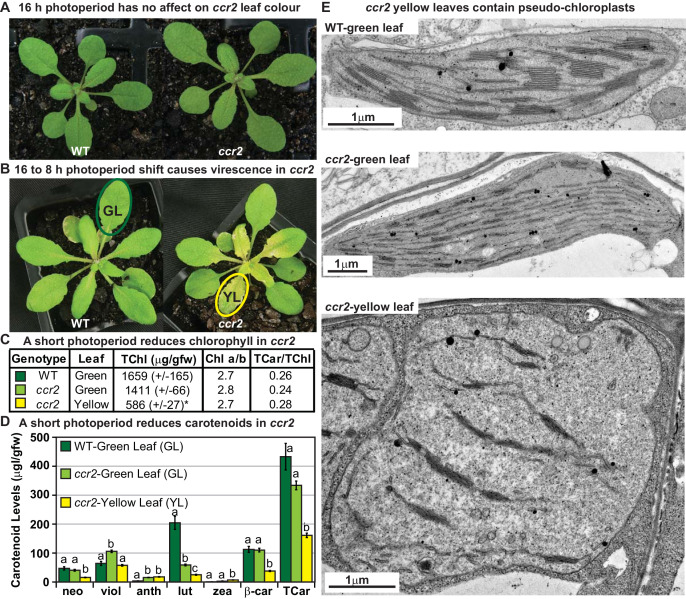
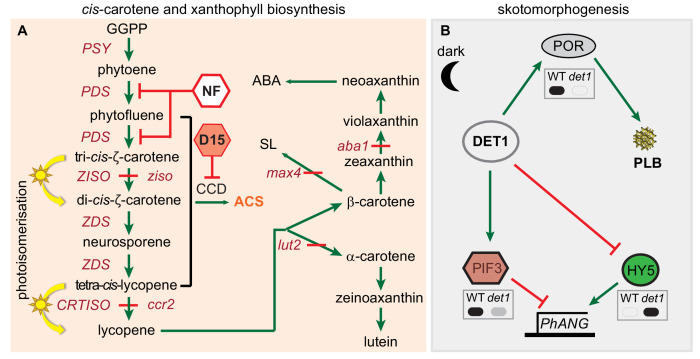
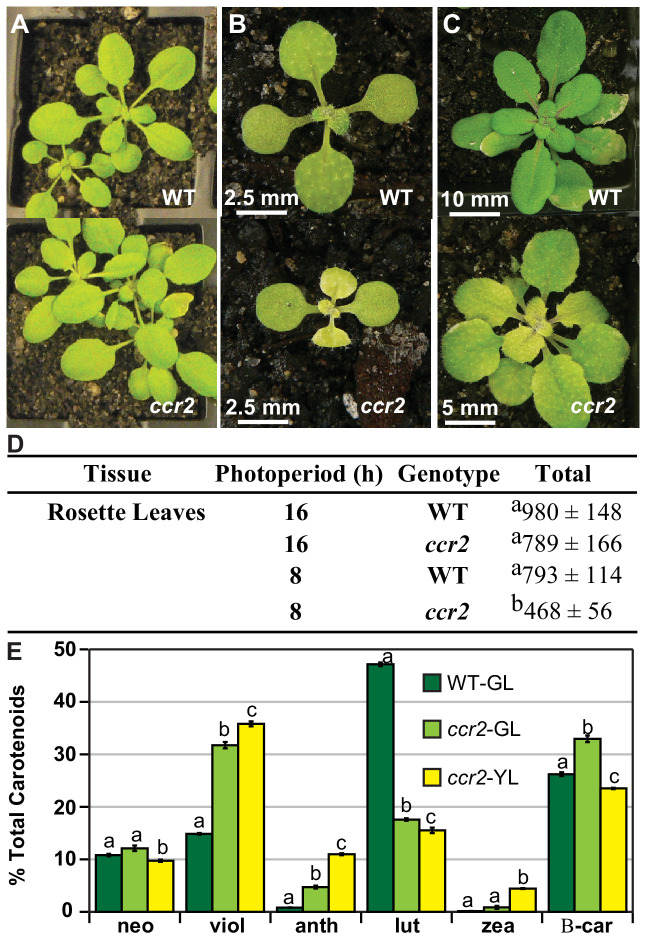
Figure 1. A shorter photoperiod alters plastid development and pigmentation in ccr2.
(A) Three-week-old wild type (WT) and ccr2 plants growing under a 16 hr light photoperiod. (B) Two-week-old plants were shifted from a 16 hr to 8 hr photoperiod for one week and newly emerged or expanded leaves appeared yellow in ccr2 (YL; yellow outline), while WT displayed green leaves (GL; green outline). (C) Chlorophyll levels (µg/gfw) and pigment ratios in green (WT and ccr2) and yellow (ccr2) leaves formed one week after a photoperiod shift from 16 hr to 8 hr. Standard error is shown for TChl (n = 5, single leaf from five plants). Star denotes significant differences (ANOVA; p<0.05). (D) Absolute carotenoid levels (μg/gfw) in green (WT and ccr2) and yellow (ccr2) leaves formed one week after a photoperiod light shift from 16 hr to 8 hr. Values represent average and standard error bars are displayed (n = 5, single leaf from five plants). Lettering denotes significance (ANOVA; p<0.05). Neoxanthin (neo), violaxanthin (viol), antheraxanthin (anth), lutein (lut), zeaxanthin (zea), β-carotene (β-car), Total Chlorophyll (TChl), Chlorophyll a/b ratio (Chl a/b), Total carotenoids (TCar). (E)Transmission electron micrograph images showing representative chloroplasts from WT and ccr2 green leaf sectors as well as yellow leaf sectors of ccr2.