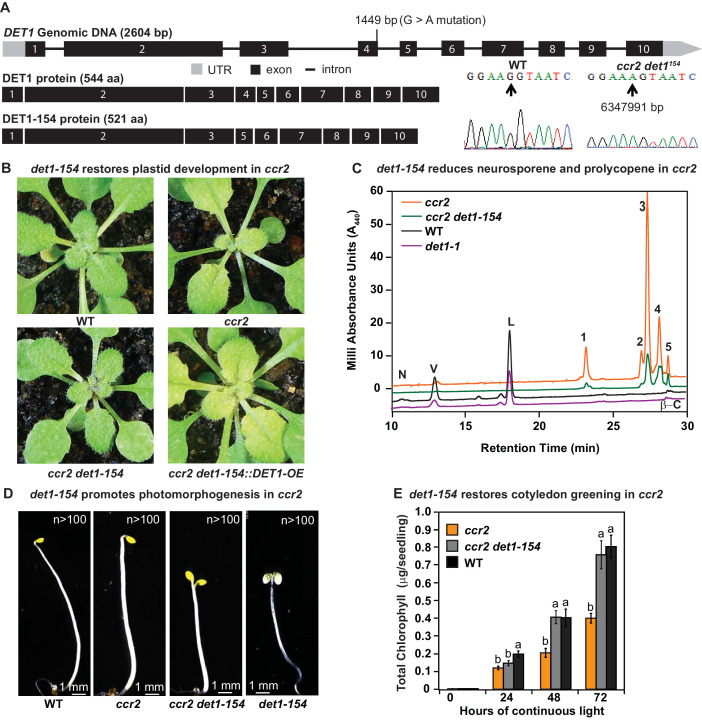
Figure 5. det1 restores PLB formation, plastid development and cotyledon greening in ccr2.
(A) Schematic structure of the wild type DET1 gDNA, DET1 protein and alternative spliced DET1-154 protein. A G->A mutation at the end of exon 4 (1449 bp) of AT4G10180 (6347991 bp) was confirmed by Sanger sequencing that leads to the skipping of exon 4 (69 bp). The DET1-154 splice variant produces a shorter protein (521 aa). Exon 4 comprises 23 amino acids in-frame, having homology to the six-hairpin glycosidase-like (IPR008928) domain. (B) Rosette images of WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154, and ccr2 det1-154::DET1-OE showing leaf pigmentations in newly emerged leaves from plants shifted from a 16 hr photoperiod (2 weeks old) to an 8 hr photoperiod for 1 week. Images are representative of 122/149 T1 generation ccr2 det1-154 plants from 12 independent lines surviving Basta herbicide selection after being transformed with pEARLEY::DET1-OE. (C) Carotenoid profiles of 7-d-old dark grown cotyledons from WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and det1-1 etiolated seedlings. Wavelengths close to the absorption maxima of A440 (major carotenoids and ζ-carotene isomers) show neoxanthin (N); violaxanthin (V); lutein (L), β-carotene (β-C) in WT and neurosporene isomers (1 and 2) tetra-cis-lycopene (3); pro-neurosporene (4), and pro-ζ-carotene (5) in ccr2 and to a less extent in ccr2 det1-154. (D) Etiolated seedling morphology of WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154. Seedlings were grown in the dark for 7 d on MS media without sucrose. Representative images (>100 seedlings from independent experiments) depict a typical apical hook for WT and ccr2, and shorter hypocotyl with open cotyledons for ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154. (E) Chlorophyll levels in cotyledons following de-etiolation. ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and WT were etiolated for 4 d in darkness and thereafter exposed to continuous white light. Chlorophyll measurements were taken at 0, 24, 48 and 72 hr after de-etiolation. Letters within a time point denote statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Tukey test (n > 20 seedlings). Error bars denote standard error of means.