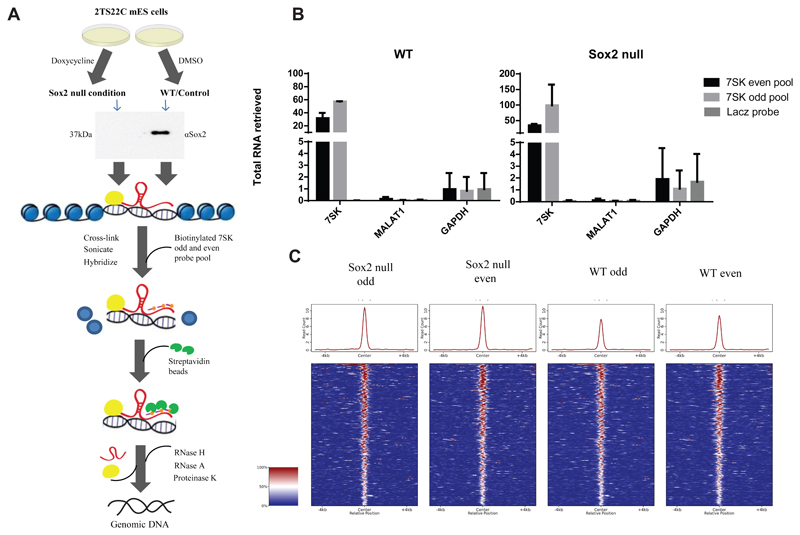
Figure 3.
A) Schematic representation of Chromatin Isolation by RNA Purification (ChIRP) strategy to assess global recruitment of 7SK to the chromatin following Sox2 KO. Doxycycline inducible Sox2 KO 2TS22C mES cells were treated with 1 μg/ml doxycycline or DMSO for 24hrs. Western blot with 30 ng of protein extract from doxycycline treated and untreated cells shows a deletion of Sox2 in the treated samples. Sox2 null and WT 2TS22C cells were cross-linked with glutaraldehyde, sonicated and hybridized to 7SK odd and even biotinylated pools (three probes per pool) or a single biotinylated probe against LacZ mRNA. Streptavidin beads were used to pull down DNA bound by 7SK and then sequenced.
B) RT-qPCR showing percent RNA pulled down following ChIRP with 7SK odd and even pools in Sox2 null and WT mES cells (n=2). Error bars indicate SD. 7SK is pulled down specifically with varying efficiencies by the 7SK odd and even pool compared to the LacZ control. Neither Gapdh nor Malat1 RNA show any significant enrichment with 7SK odd and even pools in both the conditions.
C) Comparison of global genomic 7SK binding in WT and Sox2 null conditions in 2TS22C cells. Heat map showing ChIRP-seq signal, normalized to read depth, +/- 5 Kb around peak mid-points common to 7SK odd and even data sets in Sox2 null and WT samples from two independent ChIRP experiment. There is no significant change in global genomic 7SK recruitment following Sox2 ablation.