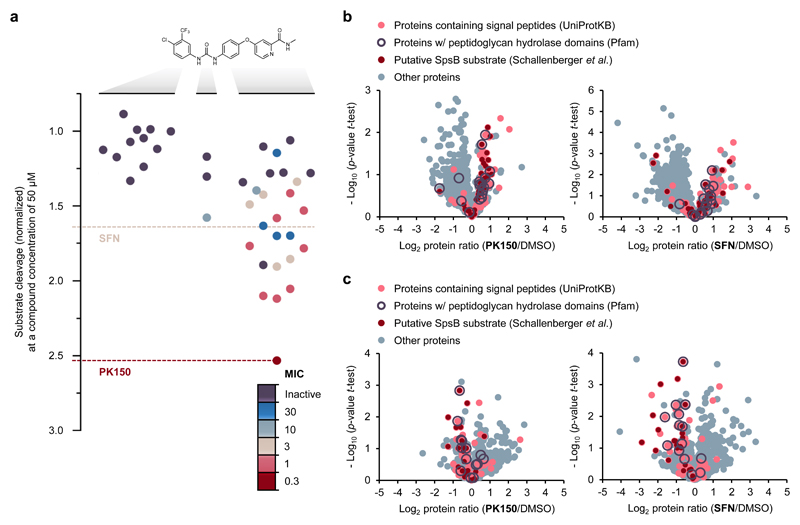
Figure 4. Structure activity relationship study of SFN and mode of action analysis by chemical proteomics.
(a) Structure activity relationship study with 40 analogues of SFN highlighting the role of various structural key elements for the activation of SpsB (boxplot) as well as antibacterial activity (colour code). Antibacterial activity was tested against S. aureus NCTC 8325; MIC values are represented according to the introduced colour code. SpsB activity was determined by a FRET-based activity assay using S. aureus NCTC 8325 membranes containing endogenous SpsB (0.2 mg/mL total membrane protein concentration; 50 μM compound concentration). Substrate cleavage rates are normalized to DMSO-treated samples. A full list of compounds, structures and activities can be found in Supplementary Data 1.
(b) Secretome analysis. Volcano plots show log2 fold change of protein levels in the secretome after treatment of S. aureus NCTC 8325 cells with PK150 (0.15 μM, 0.5-fold MIC; left panel) or SFN (1.5 μM, 0.5-fold MIC; right panel) compared to DMSO treatment. Dark red dots represent proteins whose secretion has been found to be inhibited by Arylomycin C16 (experimentally proposed SpsB substrates).35 Light red dots represent proteins that are predicted to have a SpsB signal peptide motif (according to UniProtKB as annotated by SignalP).61 Purple circles represent peptidoglycan hydrolase domain-containing proteins (Pfam annotations).60 Data represent average values and p-values were calculated using a two-sided two sample t-test; n = 4 independent experiments per group.
(c) Surfaceome analysis. Volcano plots show log2 fold change of protein levels in the surfaceome after treatment of S. aureus NCTC 8325 cells with PK150 or SFN (0.5-fold MIC) compared to DMSO. Colour coding is equivalent to panel (b). Data represent average values and p-values were calculated using a two-sided two sample t-test; n = 4 independent experiments per group.