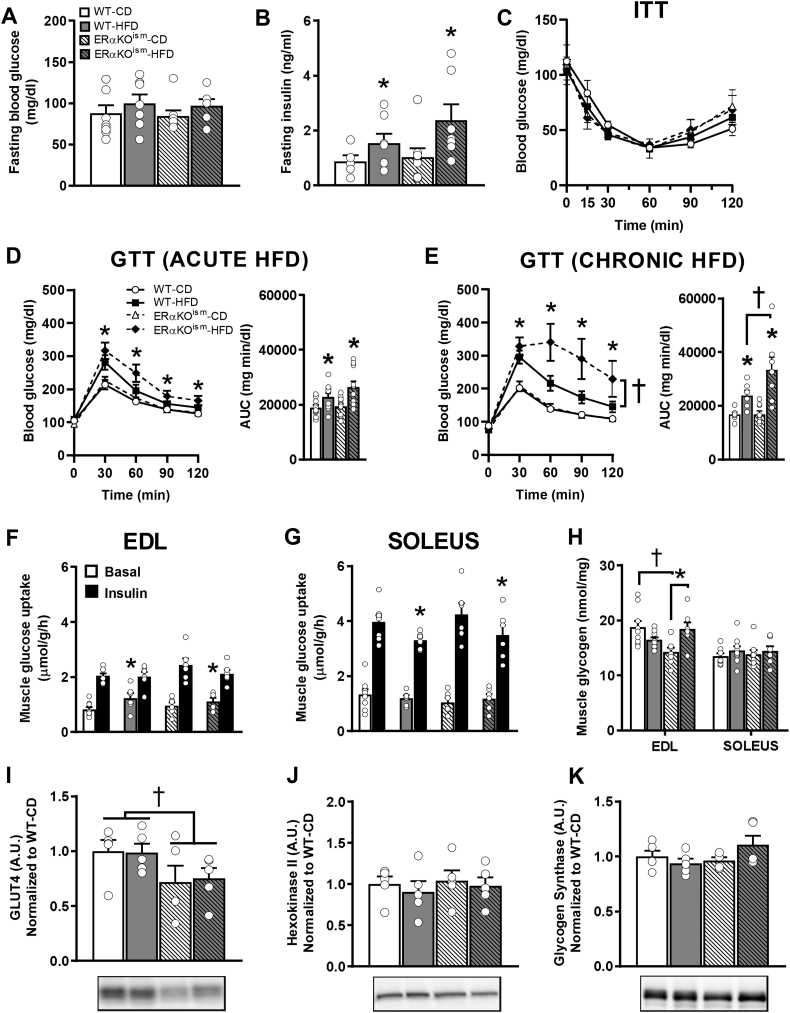
Figure 4.
A-J. Induced ablation of skeletal muscle ERα in adult female mice increases the susceptibility to develop glucose intolerance after chronic HFD treatment but does not impair skeletal muscle glucose uptake. (A, B) Fasting blood glucose (n = 6–9/group) and fasting insulin after chronic (11 weeks) HFD (n = 5–8/group). (C) Insulin tolerance test after chronic HFD (n = 5/group). (D, E) Glucose tolerance after acute (1 week) HFD (n = 10–12/group) and chronic HFD (n = 6–9/group). (F, G)Ex vivo basal and insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle glucose uptake in extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and soleus muscles (n = 6–8/group), (H) skeletal muscle glycogen content (n = 7–9/group), and (I–K) immunoblots for tibialis anterior muscle protein content of glucose transporter-4 (GLUT4), hexokinase II, and glycogen synthase after chronic HFD (n = 5/group). Data are mean ± SEM. *Main effect of diet, p < .05. †Main and simple main effects of genotype, p < .05.