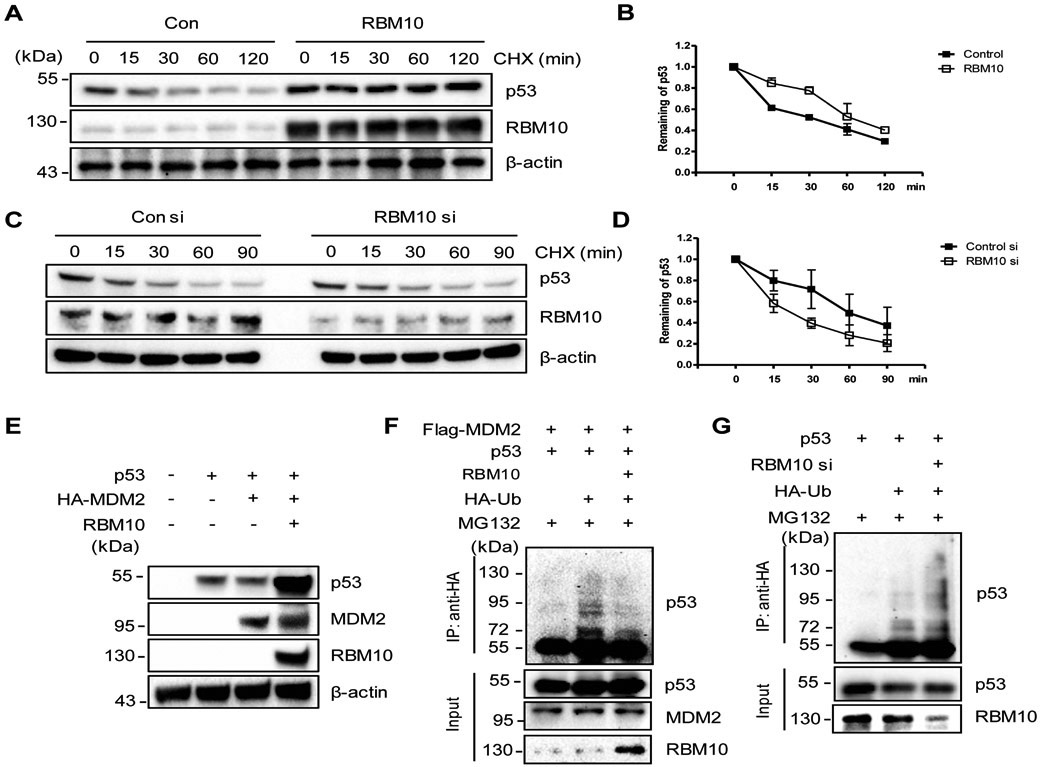
Figure 3. RBM10 inhibits MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53.
(A and B) p53’s half-life is increased upon RBM10 overexpression. HCT116p53+/+ Cells were treated with pcDNA or RBM10 for 48 h, then treated with 50 μg ml−1 of CHX, and harvested at different time points as indicated for IB analysis. (C and D) p53’s half-life is decreased upon RBM10 knockdown. HCT116p53+/+ Cells were treated with scramble or RBM10 siRNA for 72 h, treated with 50 μg ml−1 of CHX, and harvested at different time points as indicated for IB analysis. (E) HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding p53, HA-MDM2 and RBM10, respectively, and harvested 48 h post transfection for IB analysis with indicated antibodies. (F) HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding p53, Flag-MDM2, HA-Ub or RBM10, and treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h before being harvested for an in vivo ubiquitination assay. Bound and input proteins were detected by IB analysis using antibodies as indicated. (G) HCT116p53+/+ cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding p53, HA-Ub or RBM10 siRNA, and treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h before being harvested for an in vivo ubiquitination assay. Bound and input proteins were detected by IB analysis using antibodies as indicated.