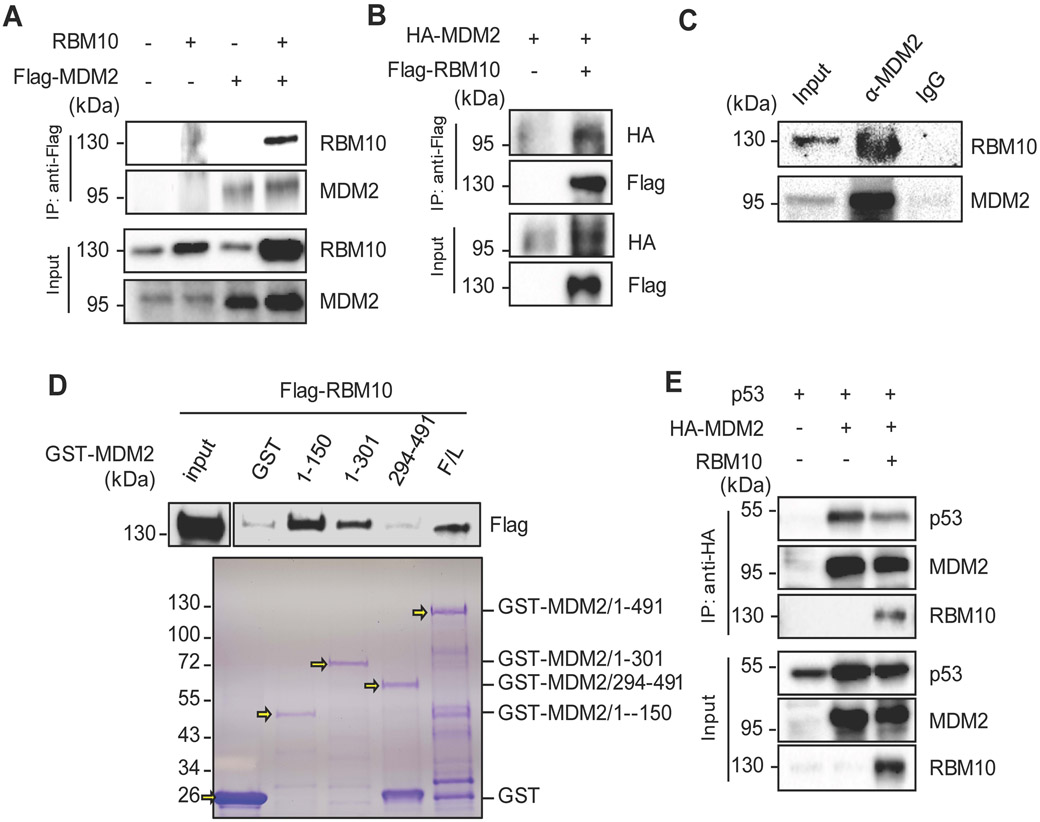
Figure 5. RBM10 interacts with MDM2.
(A and B) Exogenous RBM10 interacts with p53. HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with plasmids encoding RBM10 and Flag-MDM2 or HA-MDM2 and Flag-RBM10 as indicated followed by co-IP-IB assays using antibodies as indicated. (C) The association between endogenous RBM10 and p53 is detected in HCT116p53+/+ cells by co-IP-IB assays using antibodies as indicated. IgG was used as a control. (D) Mapping the RBM10 binding domain of MDM2 by GST-pull down assay. HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with Flag-RBM10 encoded plasmid, and the cell lysate was incubated with GST-tagged full-length MDM2 or MDM2 fragment, aa 1-150, aa 1-301 or aa 294-491, or GST protein alone. Bound proteins were detected by IB with the anti-RBM10 antibody or using coomassie staining. (E) Exogenous RBM10 inhibits p53-MDM2 binding. HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding p53, HA-MDM2 or RBM10 as indicated followed by co-IP-IB assays using antibodies as indicated.