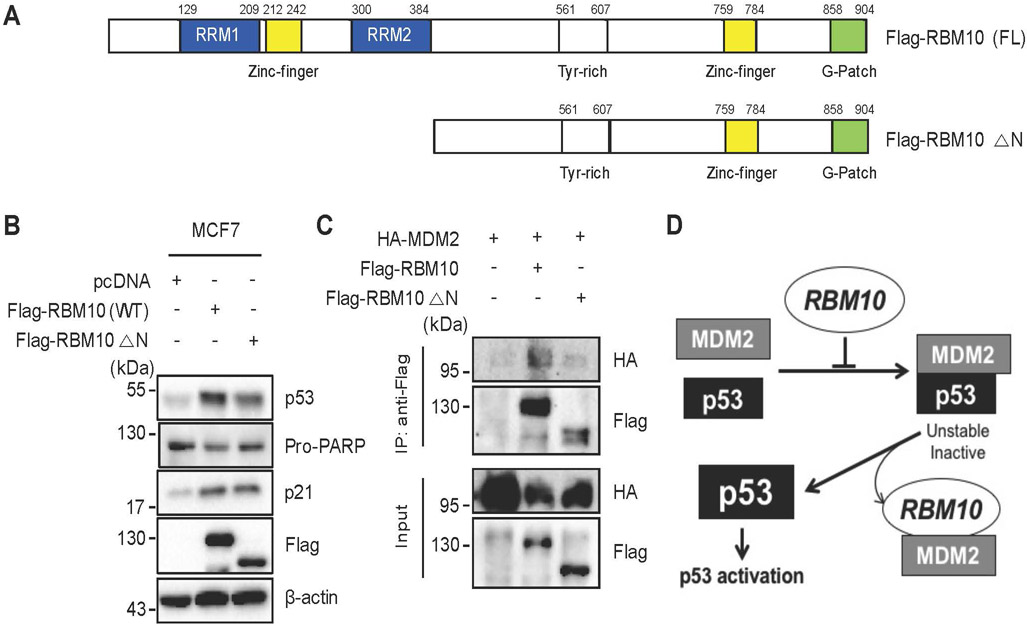
Figure 6. The RRM1- and RRM2-containing N-terminus of RBM10 is required for p53 activation.
(A) A schematic diagram of RBM10’s functional domains. (B) MCF7 cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding pcDNA, Flag-RBM10 (WT) or Flag-RBM10 (△N) and harvested 48 h post transfection for IB analysis with indicated antibodies. (C) HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding pcDNA, HA-MDM2, Flag-RBM10 (WT) or Flag-RBM10 (△N) and harvested 48 h post transfection for Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assays using antibodies as indicated. (D) A schematic for how RBM10 induces p53-dependent apoptosis and cell growth arrest by inhibiting MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53.