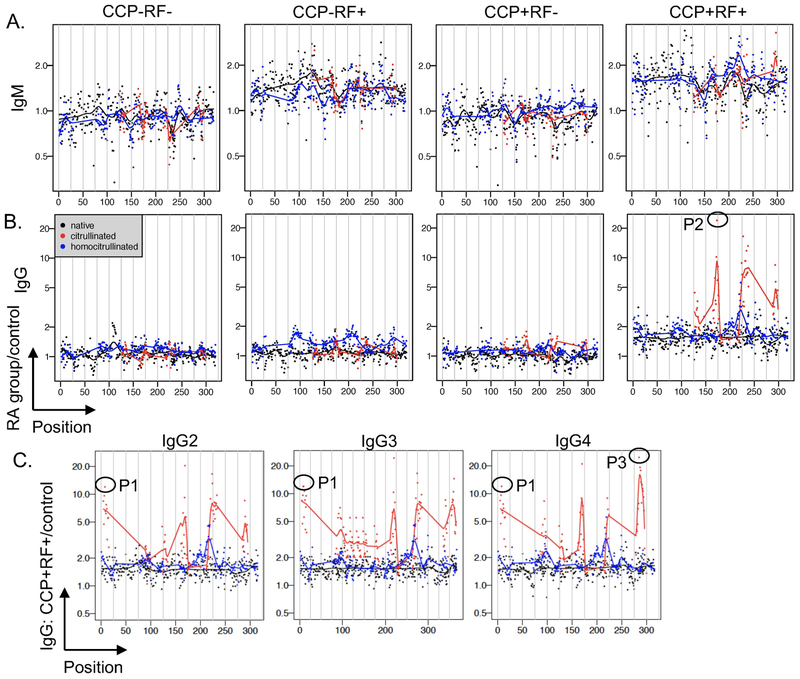
Figure 4. IgM binds IgG-derived peptides at a low level and IgG binds primarily citrulline-containing IgG peptides at a high level in rheumatoid arthritis.
Binding of IgM (A) and IgG (B) for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) subjects divided by controls is graphed for each peptide according to its position in the constant region of IgG1 for CCP-RF-, CCP-RF+, CCP+RF-, and CCP+RF+ subjects (n=12 subjects per group). C. IgG binding for CCP+RF+ RA subjects divided by controls is graphed for each peptide of the constant regions of IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 (n=12). Peptides (native and citrulline-containing versions) circled in (B) and (C) were evaluated by ELISA in Figure 5.