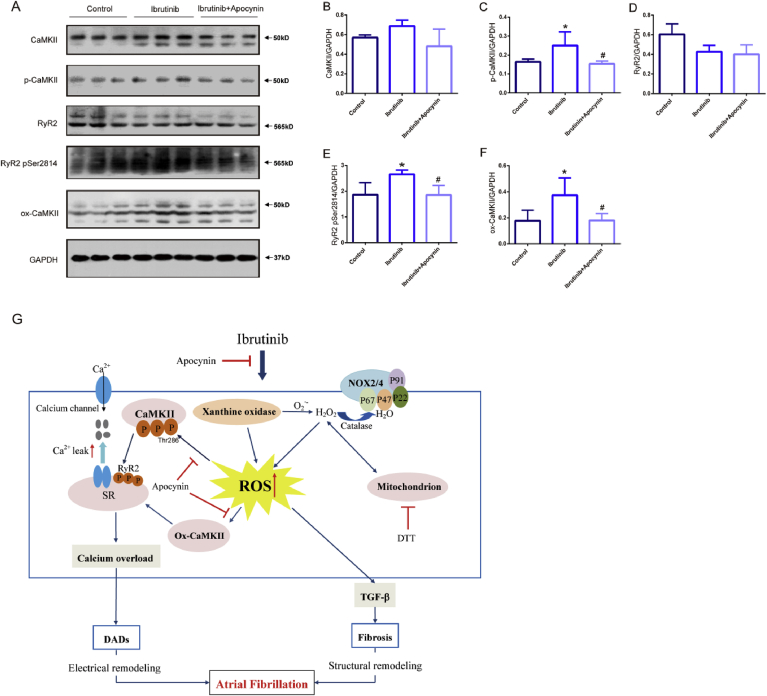
Fig. 7.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) activates oxidized Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (ox-CaMKII) increasing serine 2814 on RyR2, and the inhibitory effect of apocynin. (A–F) Representative western blots and quantification of anti-calmodulin-dependent protein kinases II (CaMKII), anti-CaMKⅡ (phospho T286, p-CaMKII), oxidized CaMKII, Ryanodine Receptor 2 (RyR2), RyR2-Ser2814 expression in the atrial tissues of mice in the control group, ibrutinib group, and apocynin group with GAPDH as a loading control (n = 3 mice per group, one way ANOVA). Values are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs Control group. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. Ibrutinib group. (G) Working model of AF-promoting mechanisms due to ibrutinib. SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RyR2, Ryanodine Receptor 2; CaMKII, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; ox-CaMKII, oxidized CaMKII; DTT, DL-Dithiothreitol; DADs, delayed afterdepolarizations; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.