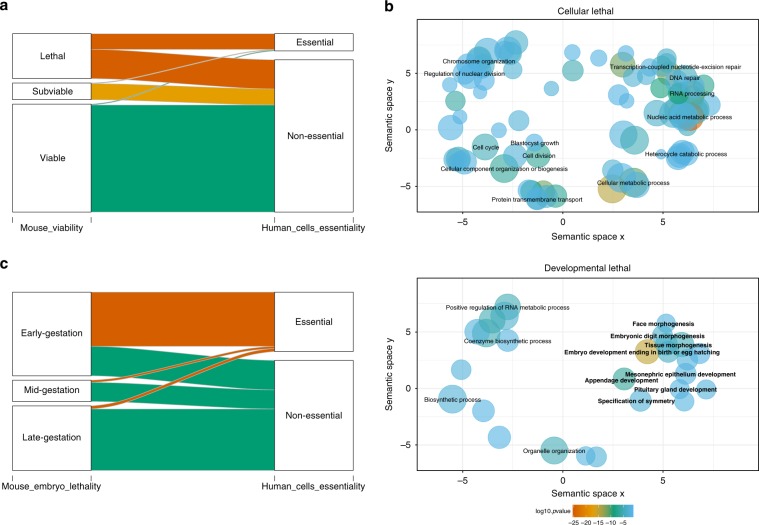
Fig. 1. Cross-species FUSIL categories of intolerance to LoF.
a Correspondence between primary viability outcomes in mice and human cell line screens. The sankey diagram shows how human orthologues of mouse genes with IMPC primary viability assessment (lethal, subviable and viable) regroup into essential and non-essential human cell categories; the width of the bands is proportional to the number of genes. b Gene Ontology Biological Process (GO BP) enrichment results. Significantly enriched GO terms at the biological process level were computed using the set of IMPC mouse-to-human orthologues incorporated into the FUSIL categories as a reference (Table 1) and identified after correcting for multiple comparisons. Significant results were only found for the cellular and developmental lethal gene categories. Bubble size is proportional to the frequency of the term in the database and the colour indicates significance level as obtained in the enrichment analysis. The GO terms associated with embryo development are in bold. c Correspondence between mouse embryonic lethality stage and essentiality in human cell lines. Embryonic lethal LoF strains are assessed for viability at selected stages during embryonic development: early (gestation) lethal (prior to E9.5), mid (gestation) lethal (E9.5–E14.5/15.5), late (gestation) lethal (E14.5/E15.5 onwards). E embryonic day.