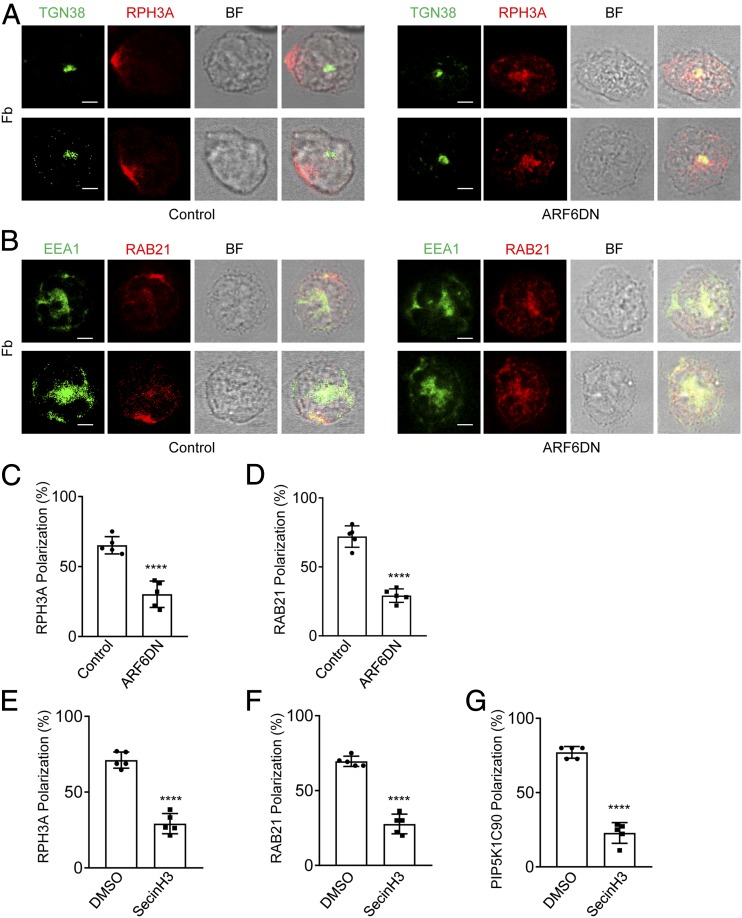
FIGURE 2.
ARF6DN and SecinH3 inhibit RPH3A and RAB21 polarization in mouse neutrophils. (A–D) ARF6 dominant-negative (DN; T27N) mutant impairs RPH3A and RAB21 polarization in mouse neutrophils. Mouse neutrophils were transfected with ARF6DN-TagRFP (ARF6DN) or TagRFP (control). The next day, RFP-positive cells were sorted out by FACS and placed on Fb-coated coverslips for 30 min, followed by immunostaining with anti-RPH3A and anti-TGN38 (A) or anti-RAB21 and anti-EEA1 (B), followed with Alexa 633 (red)– and Alexa 488 (green)–conjugated secondary Abs, respectively. Representative optical section images of two cells are shown. Quantification of polarization of RPH3A and RAB21 was performed as described in the Materials and Methods and shown in (C) and (D), respectively. Each data point represents the average of more than 15 cells per observation field, and the experiment was repeated three times. Data are present in means ± SEM (Student t test). Scale bar, 3 μm. (E–G) SecinH3 impairs RPH3A, RAB21, and PIP5K1C90 polarization in mouse neutrophils on the Fb-coated surface. Mouse neutrophils were pretreated with DMSO or 20μM SecinH3 for 20 min at room temperature (RT) and then placed on an Fb-coated coverslip for 30 min along with the DMSO or SecinH3 treatment and subjected to immunostaining with anti-RPH3A and anti-TGN38 (E), anti-RAB21 and anti-EEA1 (F), or anti-PIP5K1C90 and anti-EEA1 (G), followed with Alexa 633 (red)– and Alexa 488 (green)–conjugated secondary Abs, respectively. Quantifications of polarization of RPH3A, RAB21, and PIP5K1C90 are shown in (E)–(G), respectively. Each data point represents the average of more than 15 cells per observation field, and the experiment was repeated four times. Data are present in means ± SEM (Student t test). ****p < 0.0001. BF, bright field.