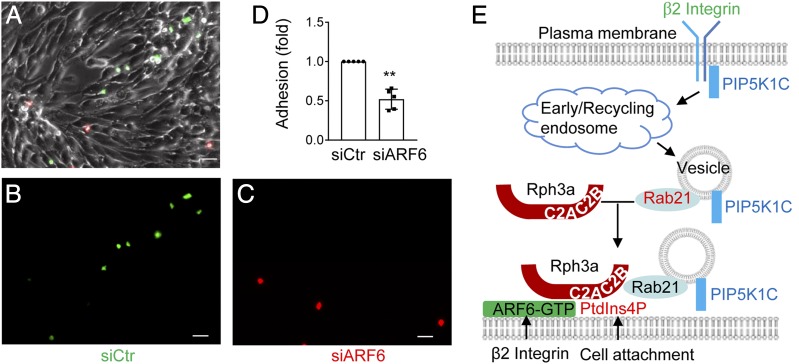
FIGURE 7.
ARF6 regulates neutrophil adhesion. (A–D) ARF6 is important for neutrophil adhesion on the inflamed endothelial layer. Mouse neutrophils were transfected with siCtr or siARF6 for 48 h and were labeled with CFSE and Far Red dyes, respectively, then mixed at 1:1 ratio before flowing through a chamber seeded with endothelial cells pretreated with TNF-α. The adherent neutrophils were imaged under a widefield microscope. Representative images of bright field (A), CFSE (B), and Far Red (C) are shown. The adhesion quantification of the siCtr- or siARF6-transfected neutrophils is also shown (D). Each data point represents one chamber, and the experiment was repeated five times. Data are present in means ± SEM (Student t test). Scale bar, 50 μm. **p < 0.01. (E) Schematic presentation of a model for ARF6 to direct polarized docking of RPH3A–PIP5K1C90 vesicles at the PM. Integrin engagement triggers endocytosis of PIP5K1C90, which traffics through EEA1-positive endosomes and RAB21-positive recycling vesicles, and the GTP-bound RAB21 exits from the endosomes and recruits RPH3A (16), which, in turn, targets the vesicles to PM PtdIns4P with the help of the coincidence-detection code of ARF6, where the PM PtdIns4P polarization is induced by cell attachment (17). This process eventually results in PIP5K1C90 polarization and confers neutrophil adhesion on inflamed endothelium.