Fig. 1.
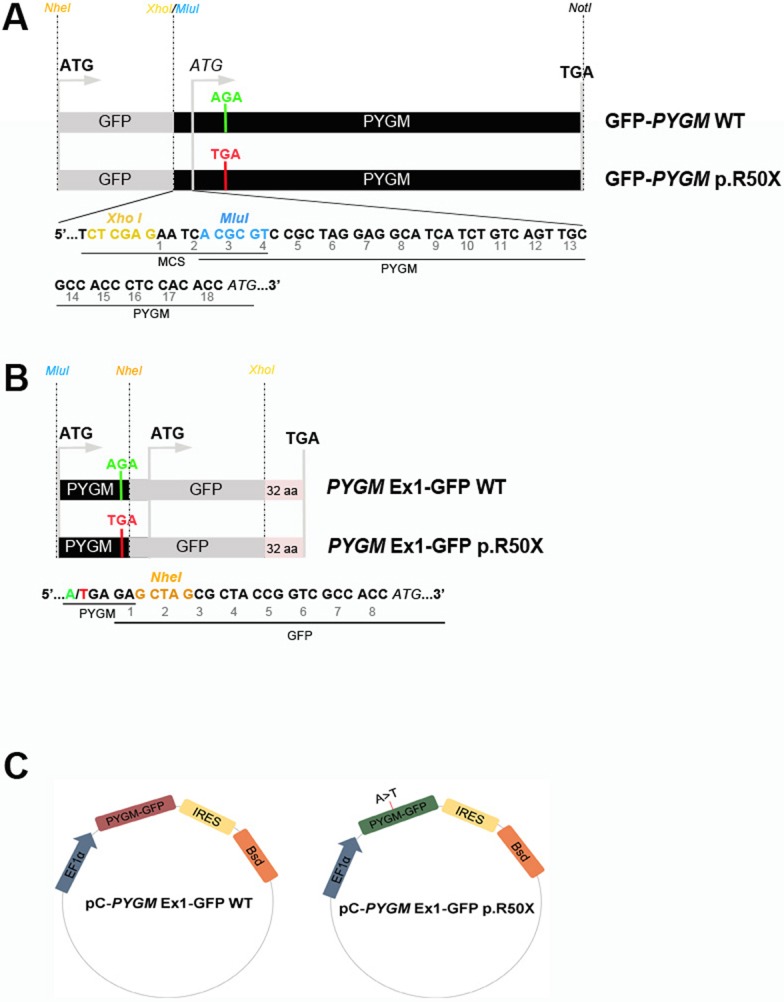
GFP-PYGM plasmid constructs used to analyze p.R50X Pygm read-through. (A-C) Different GFP-PYGM constructs were transiently (A,B) and stably (C) transfected in HeLa and HEK293T cells, respectively. (A) The GFP-PYGM wild-type (WT) and p.R50X constructs included the GFP encoding sequence followed by the full-length mouse Pygm cDNA encoding sequence, and varied in the absence or presence of the p.R50X mutation. The XhoI restriction site (yellow) disrupted the GFP coding sequence corresponding to the last 20 amino acids of the GFP protein. The MluI (blue) restriction site was used to insert the Pygm cDNA into the pCI-neo multicloning site. (B) The PYGM Ex1-GFP WT and p.R50X constructs consisted of the mouse exon 1 Pygm cDNA encoding the first 50 amino acids of the GP-M protein followed by the GFP encoding sequence. MluI (blue) and NheI (orange) restriction sites were used to insert the Pygm sequence, while NheI and XhoI (yellow) restrictions sites were used to insert the GFP encoding sequence into the pCI-neo multicloning site. (C) Structure of pC-PYGM EX1-GFP WT (left) and pC-PYGM-EX1-GFP p.R50X (right). EF1α, elongation factor 1α; GFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; IRES, internal ribosomal entry site; Bsd, blasticidin S resistance gene.
