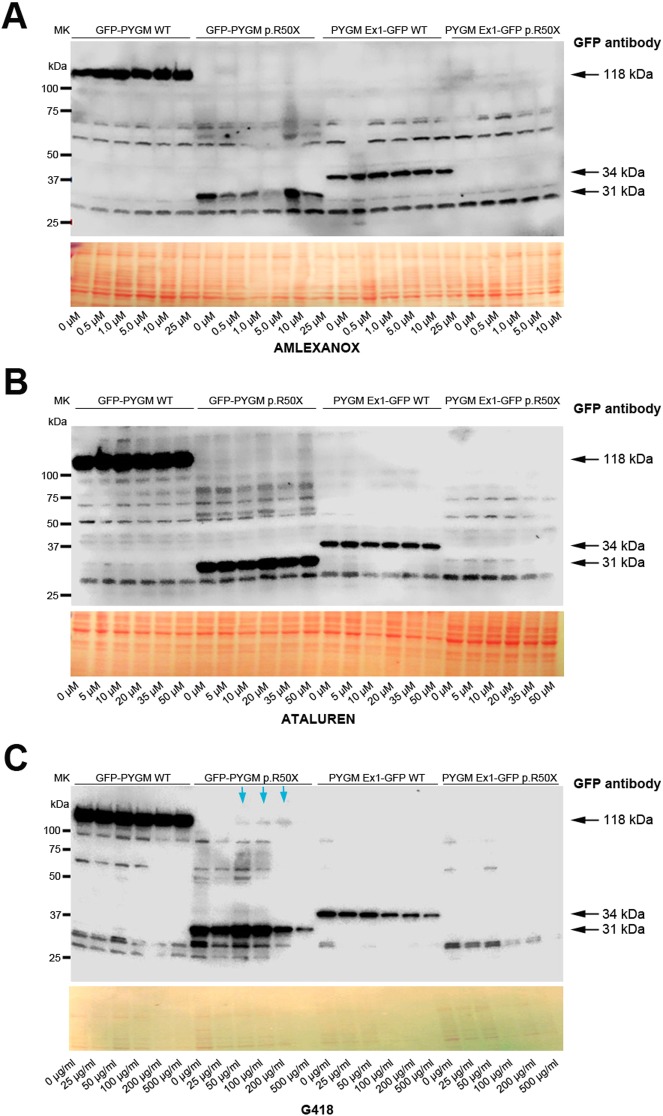
Fig. 4.
Read-through analysis in transient transfected cells. (A-C) Read-through analysis in HeLa cells transfected with WT, p.R50X GFP-PYGM and PYGM-GFP plasmids after 72 h treatment with amlexanox (A), Ataluren (B) and G418 (C). The GFP-PYGM WT plasmid generates a fusion protein of 1079 amino acids and a molecular weight of 118 kDa, consisting of the N-terminal GFP protein (219 amino acids) fused to the full-length PYGM protein (18 amino acids from the 5′UTR+842-amino-acid full-length protein). In the absence of read-through induction, the GFP-PYGM p.R50X plasmid generates a fusion protein of 286 amino acids (GFP 219 amino acids+18 amino acids PYGM 5′UTR and 49 amino acids from PYGM coding sequence) and a molecular weight of 31 kDa. The PYGM-Ex1 GFP WT plasmid generates a fusion protein of 309 amino acids and molecular weight of 34 kDa, consisting of the first 50 amino acids of the GP-M protein fused to the 219 amino acids from the GFP coding sequence and the 40 unspecific extra amino acids (8 and 32 in the N- and C-terminus of GFP protein, respectively) derived from the cloning process. Finally, in the absence of read-through induction, the PYGM-Ex1 GFP p.R50X plasmid generates a protein consisting only of the first 49 amino acids (∼5 kDa) of the GP-M protein. Blue arrows in C indicate potential read-through obtained for the GFP-PYGM p.R50X construct after treatment with G418, which could not be replicated in further experiments.