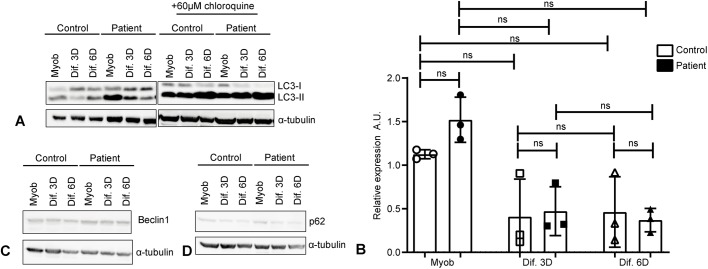
Fig. 5.
Myotubes have increased autophagic flux observed by increased Lc3-II levels after chloroquine treatment. XMEA-derived myotubes have increased levels of Lc3-II after chloroquine treatment and decreased p62 levels, indicating an increase in autophagic flux. (A) Representative images of Lc3 western blotting in cells with or without chloroquine treatment, showing that myoblasts have increased Lc3-II levels. Chloroquine treatment further increased Lc3-II in myotubes, but not myoblasts, indicating an increase in autophagy flux with differentiation. (B) Densitometric quantification showed a tendency for higher basal Lc3-II levels in myoblasts. Three independent experiments were performed. Individual points were plotted±s.d. ns, non-significant. One-way ANOVA (P=0.0327) with Dunn's post hoc for multiple comparisons. (C) Representative images of beclin 1 western blotting showing that its levels do not change with differentiation or XMEA pathology. Three independent experiments were performed. (D) Representative images of p62 western blotting showing that there is a slight decrease in p62 content in myotubes, especially XMEA-derived ones. Three independent experiments were performed. A.U., arbitrary units.