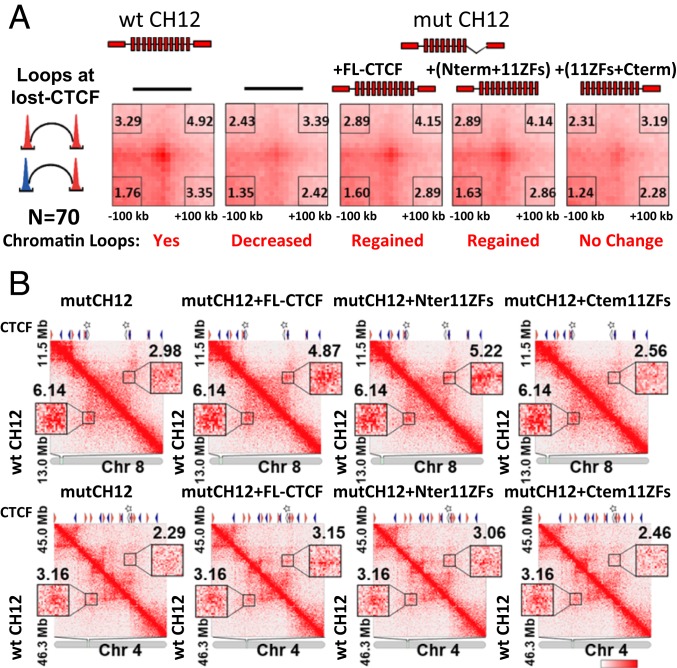
Fig. 4.
The CTCF N terminus is necessary for chromatin loop formation. (A) Chromatin loops were analyzed by Hi-C in the five types of cells (WT CH12, mut CH12, and mut CH12 cells stably expressing either of three CTCF constructs: FL-CTCF, N terminus+11ZFs, and C terminus+11ZFs). APA was performed on chromatin loops affected in mut CH12 cells compared to WT CH12 cells. Seventy loops that associated with at least one lost CTCF site (>300-kb looping range) were selected for the analysis in the five types of cells. Peak signal strength is indicated as the ratio of the central pixel to the lower left pixels in each heatmap. (B) Hi-C contact matrices showing examples of chromatin loops at the lost CTCF sites. Lower triangles show Hi-C signal from WT CH12 and upper triangles show Hi-C data from cells expressing the indicated form of exogenous CTCF. The orientation of CTCF sites is shown by orange (+ strand) or blue (− strand) triangles and the lost CTCF sites are indicated by stars.