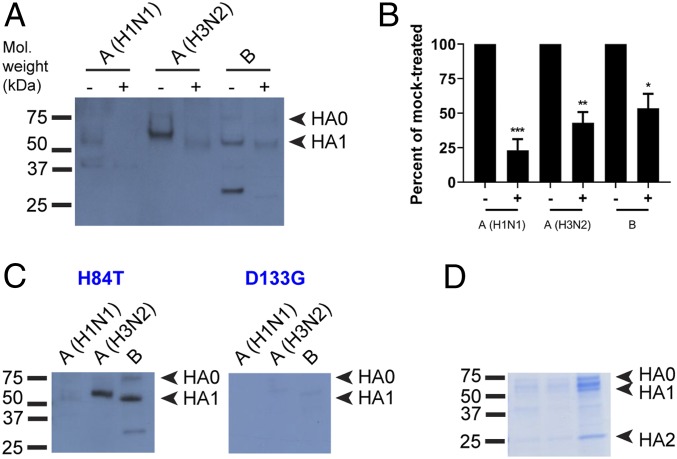
Fig. 3.
H84T binds to virus-derived HA. (A) Lectin blot. Virus particles from A/Florida/3/2006 (H1N1), A/Perth/16/2009 (H3N2), and B/Brisbane/60/2008 were lysed for protein extraction. Proteins were incubated with PNGaseF to remove N-glycans or with PBS (mock) overnight, then resolved by reducing SDS/PAGE and blotted. Blots were incubated with 100 nM H84T, followed by primary and secondary antibody incubations to detect BanLec bound to viral proteins. Note that the lower band seen in the influenza B lanes does not appear to be HA2 as it does not run at the correct size. Mol. weight, molecular weight. (B) Percent binding of H84T to PNGase- versus mock-treated HA1 in A, relative to mock-treated set at 100%. Data in A and B are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, as compared to the mock-treated group. Error bars denote the SEM. +, PNGase F-treated; −, mock-treated. (C) Lectin blots were performed as in A, without PNGase F digestion. Blots were incubated with 100 nM H84T or D133G BanLec. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Proteins were resolved as in C but not transferred and gels stained with a Coomassie-based reagent.