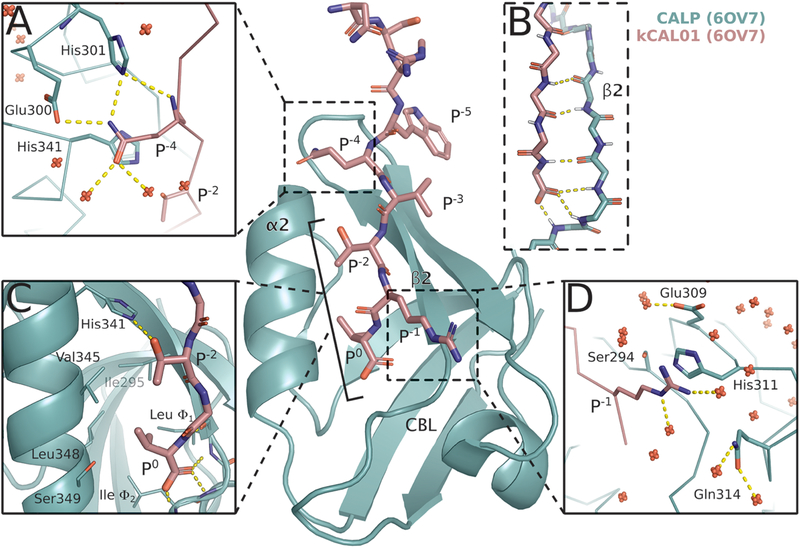
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of CALP:kCAL01 (PDB ID: 6OV7) displays canonical class 1 PDZ binding and favorable interactions at P−1 and P−4. The CALP and kCAL01 crystal structures are shown in green and pink, respectively (protomer A). Hydrogen bonds predicted by the Probe78 software are represented as dashed yellow lines. The kCAL01 peptide binds in the groove defined by helix α2 and strand β2. (A) Gln P−4 makes favorable hydrogen bonds with Glu300 or His301 and forms van der Waals interactions with His341. Additionally, Gln P−4 can coordinate with several water molecules, shown as red, nonbonded oxygens. (B) kCAL01 binds in the groove defined by helix α2 and strand β2 and forms an antiparallel β-sheet interaction with strand β2. The C-terminus of kCAL01 forms favorable hydrogen bonds with the carboxylate-binding loop (CBL). (C) kCAL01 displays features of class 1 PDZ binding,28 including the conserved hydrogen bond between Thr P−2 and His341, as well as the interaction between the Val P0 side chain and the hydrophobic pocket. (D) Arg P−1 appears to form favorable π-interactions with His311 and also coordinates with several waters.