Fig. 3.
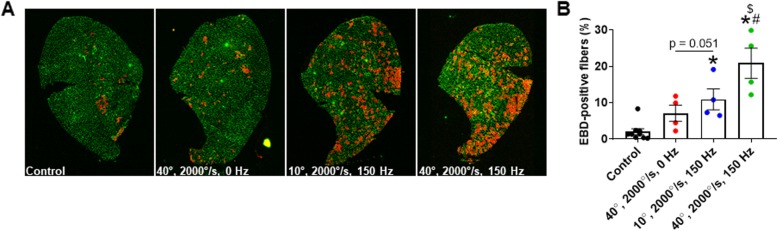
Mechanical factors of an ECC impact sarcolemmal permeability of mdx anterior crural muscles in vivo. a Fluorescent microscopy for Evan’s blue dye (EBD; red) and laminin (green) of mdx tibialis anterior muscle exposed to three eccentric contraction protocols that vary by angle change (10° and 40°) and stimulation frequency (0 and 150 Hz). b Quantification of the percentage of EBD-positive fibers in mdx tibialis anterior muscle subjected to one of three eccentric contraction protocols. No ECC = contralateral tibialis anterior not subjected to eccentric contractions, ECC = subjected to eccentric contractions. *Different from control; # 40°, 2000°/s, 0 Hz; $10°, 2000°/s, 150 Hz. Data are mean ± S.E.M with significance set at p < 0.05. N = 4/protocol