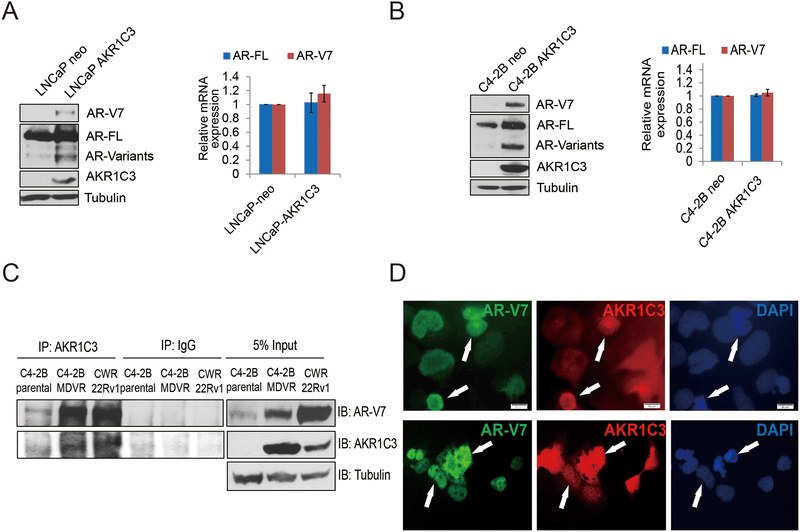
Figure 2. AKR1C3 induces AR/AR-V7 protein expression.
A. LNCaP-neo and LNCaP-AKR1C3 were cultured in FBS conditions for 5–7 days, whole cell lysates were harvested and subjected to western blot. AR-V7, AR-FL, and AKR1C3 expression was determined and tubulin was used as internal control. Total RNA was extracted and the mRNA levels of AR, AR-V7 and AKR1C3 were determined by qRT-PCR. B. C4–2B-neo and C4–2B-AKR1C3 cells were cultured in FBS conditions for 5–7 days, whole cell lysates were harvested and subjected to western blot. AR-V7, AR-FL, and AKR1C3 expression was determined and tubulin was used as internal control. Total RNA was extracted and the mRNA levels of AR, AR-V7 and AKR1C3 were determined by qRT-PCR. C. C4–2B, C4–2B MDVR and CWR22Rv1 cells were cultured in FBS condition and whole cell lysates were immunopreciptated with anti-AKR1C3 antibody and blotted with indicated antibodies. D. 293 cells were co-transfected with AR-V7, and AKR1C3 for 3 days, AR-V7 and AKR1C3 were visualized by dual immunofluorescence staining. White arrows indicated the typical staining cells in each group.