Figure 5.
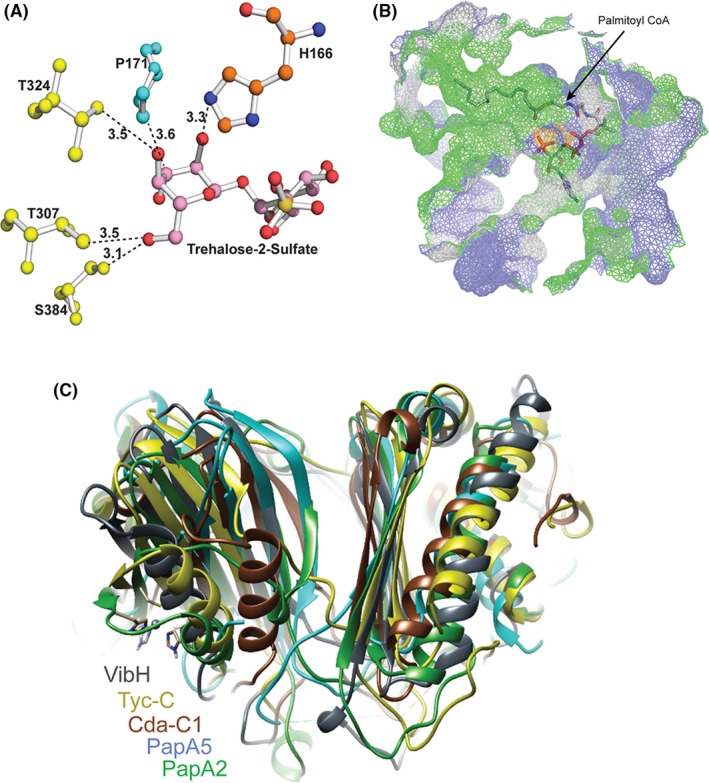
Detailed analysis of the acceptor and donor substrate binding sites. A, Ball and stick model of the substrate binding sites. The 2'‐OH group of acceptor substrate is in proximity to ε nitrogen of H166 of condensation motif, with P171, T307, T324, and S384 being additional residues in proximity to the acceptor substrate. B, Mesh surface representation shows the donor substrate conformer with the acyl component residing in a hydrophobic tunnel and the CoA component in close proximity of the tail region of the solvent accessible tunnel. C, Superposition of PapA2 with other stand‐alone C domain structures revealed a distinct NRPS C domain architecture
