Figure 1.
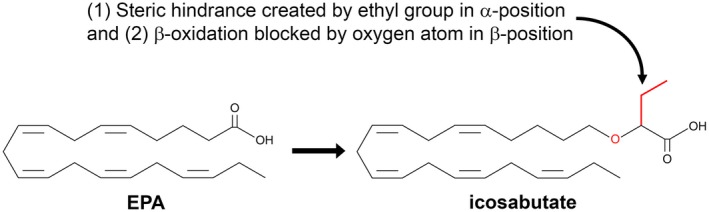
Chemical structure of icosabutate as compared with EPA. Icosabutate, a structurally engineered EPA derivative, is structured (1) to remain in a free acid form by resisting incorporation into complex cellular lipids (through an ethyl group in the α‐position) and (2) to minimize metabolism by way of β‐oxidation (through an oxygen atom substitution in the β position).
