Figure 5.
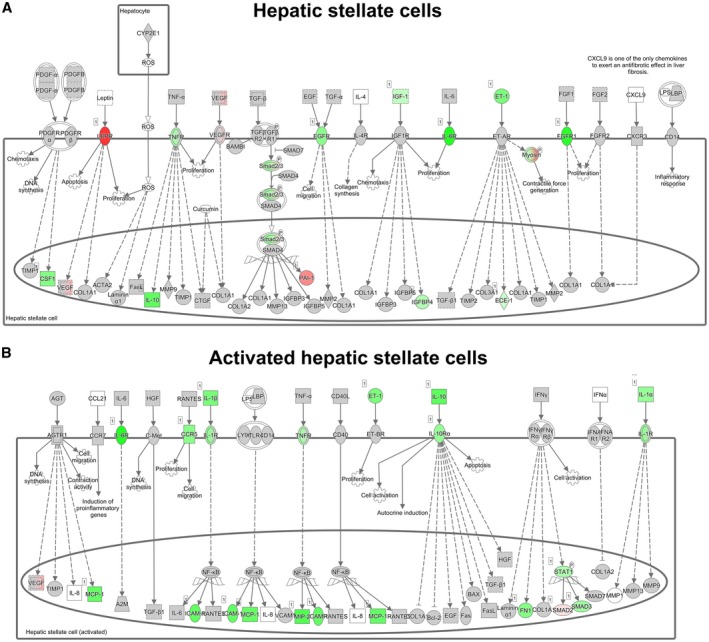
Hepatic fibrosis pathway analysis. Pathway analysis showing statistically significant gene‐expression changes in hepatic stellate cells (A) and activated hepatic stellate cells (B) of APOE*3Leiden.CETP mice fed a high‐fat/cholesterol diet and treated with icosabutate for 20 weeks relative to control group. Red color indicates up‐regulation and green color indicates down‐regulation. Abbreviations: BAX, B cell lymphoma 2–associated X protein; Bcl2, B cell lymphoma 2; CD, clusters of differentiation; CCL2, chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 2; CCR9, chemokine (C‐C motif) receptor 9; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; GSF1, growth stimulating factor 1; EGF, endothelial growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FN1, fibroblast growth factor–inducible 1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; ICAM, intercellular cell adhesion molecule; IFN, interferon; IGF, insulin‐like growth factor; LBP, lipopolysaccharide‐binding protein; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MCP‐1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; PDGF, platelet‐derived growth factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SMAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog; TGF, transforming growth factor; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; VCAM1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
