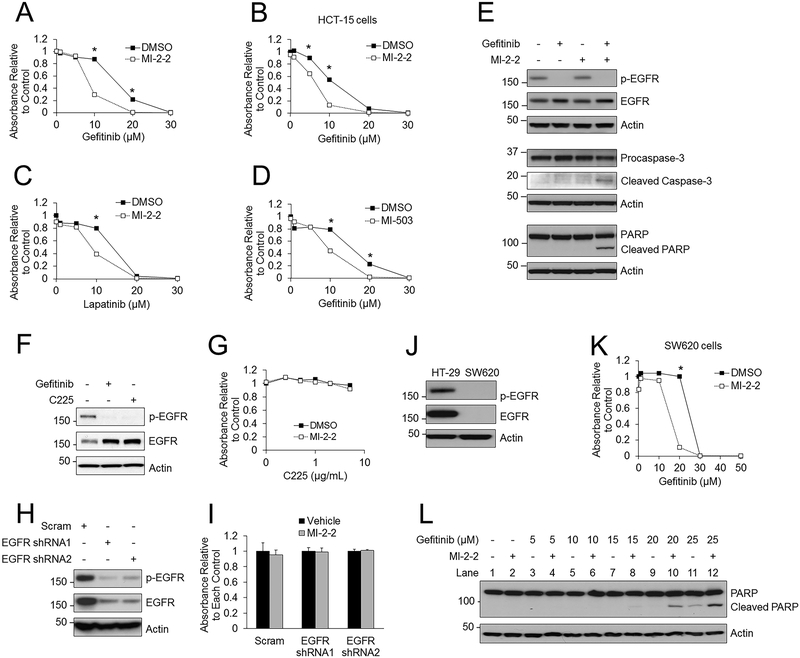
Figure 2: Menin inhibition sensitizes colon cancer cells to iEGFRs in an EGFR-independent manner.
A) Treatment of HT-29 cells with various concentrations of gefitinib, with and without 1 μM MI-2–2, with cell growth assessed after 96 hours by the MTS assay. B) HCT-15 cells treated with varying concentrations of gefitinib with and without 1 μM MI-2–2. MTS assay performed after 96 hours. C) HT-29 cells treated with varying concentrations of lapatinib with and without 1 μM MI-2–2. MTS assay performed after 96 hours. D) HT-29 cells treated with varying concentrations of gefitinib with and without 1 μM MI-503. MTS assay performed after 96 hours. E) HT-29 cells treated for 96 hours followed by analysis of protein levels by western blotting, 10 μM gefitinib, 1 μM MI-2–2. F) HT-29 cells treated for 96 hours and then analyzed by western blotting. 10 μM gefitinib, 1 μg/mL C225. G) HT-29 cells treated with varying concentrations of C225 with or without 1 μM MI-2–2 for 96 hours, and then cell growth was assessed by the MTS assay. H) HT-29 cells transduced with scrambled or EGFR shRNAs, with EGFR protein expression analyzed by western blot. I) Scrambled and EGFR shRNA transduced HT-29 cells were treated with vehicle or 1 μM MI-2–2 for 96 hours, and then cell growth was assessed by the MTS assay. J) EGFR expression was assessed by western blotting in HT-29 and SW620 cells. K) SW620 cells treated with varying concentrations of gefitinib with and without 1 μM MI-2–2. MTS assay was performed after 96 hours to assess cell growth. L) SW620 cells treated with varying concentrations of gefitinib with and without 1 μM MI-2–2 for 96 hours, then protein levels were analyzed by western blotting. * p < 0.05.