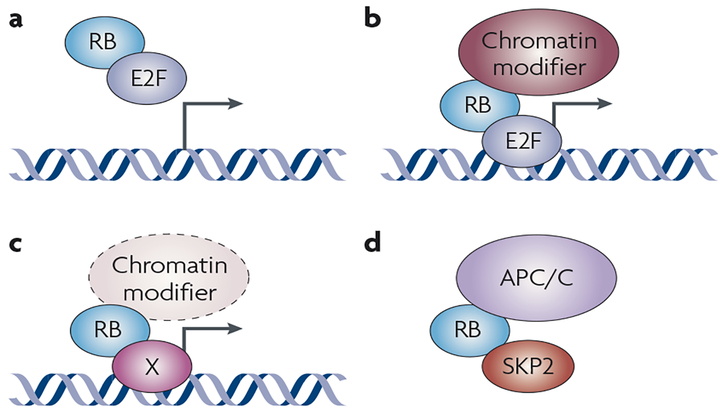
Figure 1 |. RB is a transcriptional co-factor and an adaptor protein that can function through at least four different types of protein interaction.
a | Classically, RB (retinoblastoma) binds to E2F transcription factors and recruits them away from their target genes. b | Alternatively, RB is recruited to the promoter of target genes by E2F and inhibits their transactivation activity and further recruits chromatin remodelling complexes (including HDAC (histone deactylase), DNMT1 (DNA methyltransferase 1), HP1A (heterochromatin protein 1A) and SUV39H1) to repress transcription. c | RB is a transcriptional co-factor for non-E2F transcription factors or other co-factors, such as the HIF1α (hypoxia-induced factor 1α), MYOD and SP1 transcription factors. d | RB serves as a non-chromatin-associated protein adaptor: illustrated is one example of RB acting to recruit APC/C (anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome) and SKP2 (S-phase kinase-associated protein 2) to the same complex, promoting SKP2 degradation.