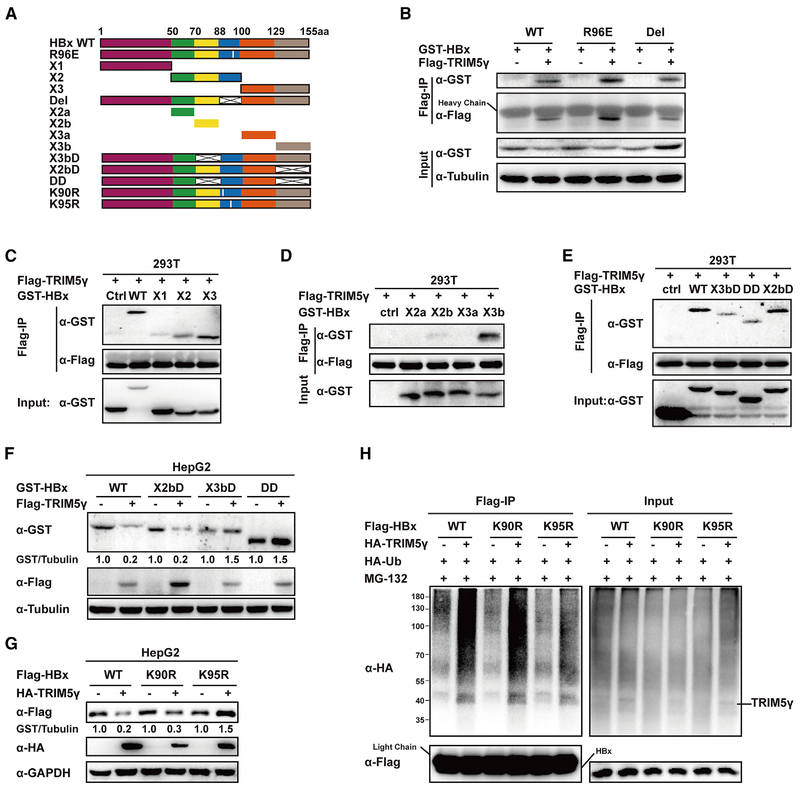
Figure 6. TRIM5γ Interacts with the C Terminus of HBx and Promotes HBx K95 Site Ubiquitination.
(A) Diagram of mutant HBx constructs. the numbers indicate the amino acids in the HBx constructs. (B–E) 293T cells were co-transfected with the expression vectors for Flag-TRIM5γ and GST-HBx WT or mutants (B, R96E, Del; C, X1, X2, X3; D, X2a, X2b, X3a, X3b; E, X3bD, DD, X2bD) or EV as indicated. After 28 h, cells were harvested, coIP with FLAG-HBx, and cell lysates and precipitated samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (F) HBx WT or truncations were co-transfected with TRIM5γ or EV into HepG2 cells; 28h later, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. (G) Plasmids of expression of HBx WT, K90R, or K95R were co-transfected with TRIM5γ or EV into HepG2 cells; 28h later, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. (H) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with the expression vectors for HA-TRIM5γ, HA-Ub, and FLAG-HBx WT or mutants as indicated; 28h later, cells were harvested and coIP with FLAG-HBx, and cell lysates and precipitated samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.