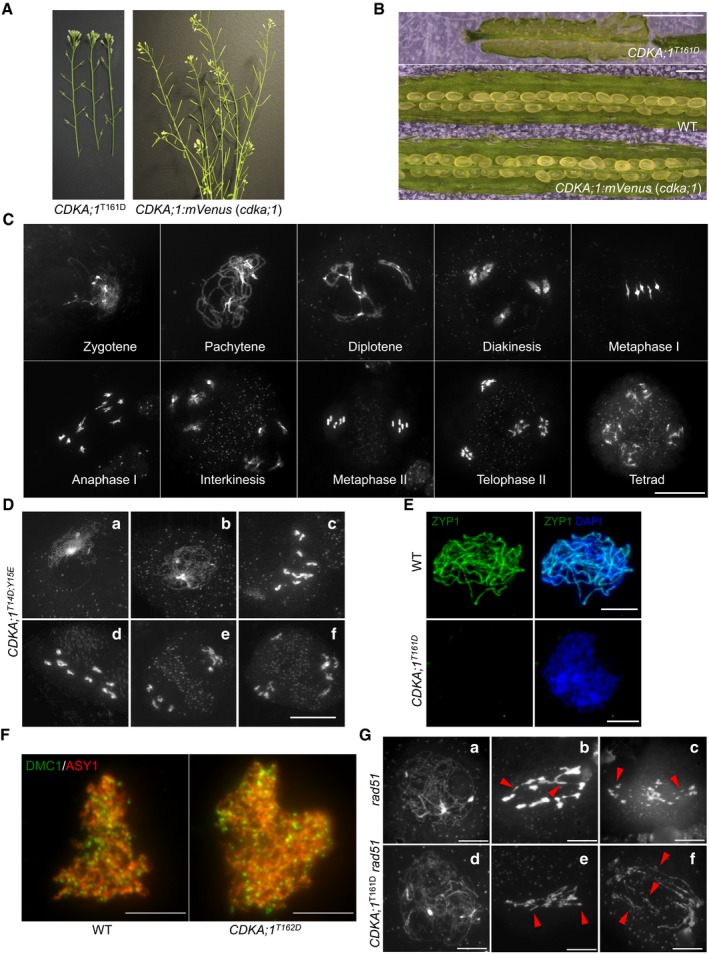
The stems of a hypomorphic cdka;1 mutant CDKA;1
T161D are completely sterile as indicated by short siliques in contrast to homozygous cdka;1 mutant expressing the CDKA;1:mVenus reporter construct that form long siliques and are full fertile.
The siliques of hypomorphic CDKA;1
T161D do not harbor viable seeds in contrast to homozygous cdka;1 mutant expressing CDKA;1:mVenus that develop healthy and plump seeds. Scale bars: 1 mm.
Chromosome spread analysis of male meiocytes of a homozygous cdka;1 mutant expressing a functional CDKA;1:mVenus reporter reveals a wild type‐like meiotic program. Scale bar: 20 μm.
Chromosome spread analysis of the hypomorphic cdka;1 mutant CDKA;1
T14D;Y15E. (a) zygotene‐like stage; (b) pachytene‐like stage; (c, d) diakinesis‐like stages; and (e, f) end of meiosis I with two or three pools of chromosomes. Scale bar: 20 μm.
Immunolocalization of ZYP1 (green) in wild‐type (WT) and CDKA;1
T161D mutants. Chromosomes are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars: 5 μm.
Immunolocalization analysis of DMC1 (green) together with ASY1 (red) in late leptotene of male meiocytes of wild‐type (WT) and CDKA;1
T161D mutants. Scale bars: 5 μm.
Chromosome spread analysis of rad51 and rad51 CDKA;1
T161D mutants. (a, d) pachytene‐like stage; (b, c, e, and f) anaphase I‐like stage. Red arrowheads indicate the chromosomal fragments. Scale bars: 10 μm.