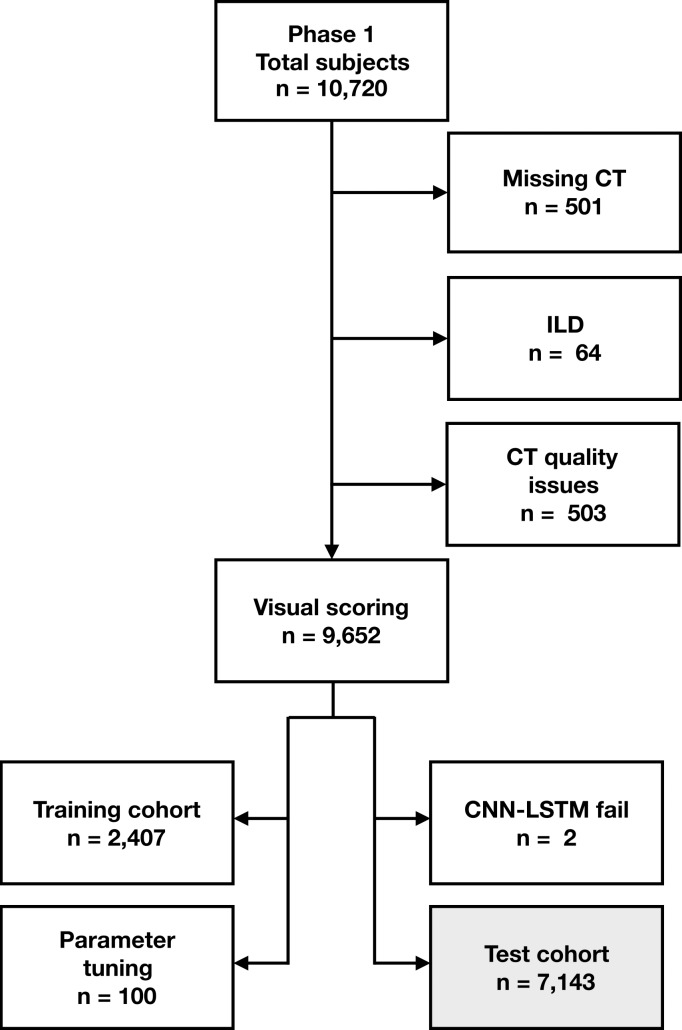
Figure 2a:
Flowchart shows participant selection. (a) Among 10 192 participants enrolled in Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) phase 1, CT was missing in 501 participants. Sixty-four participants were excluded due to presence of interstitial lung disease (ILD) and 503 CT scans were excluded due to quality issues (eg, significant artifact or scanning protocol deviation). Total of 9652 had baseline CT with visual emphysema scores and mortality data. CT scans with visual scores were partitioned into subsets of 2407, 100, and 7143 scans for training, validation, and parameter tuning and testing, respectively. Training scans were selected because they had not been included in previous analysis. Source.—Reference 5. Deep learning algorithm failed to produce results on two CT scans. (b) Among 2746 participants enrolled in Evaluation of COPD Longitudinally to Identify Predictive Surrogate End-points (ECLIPSE), 456 were missing CT and/or pulmonary function testing (PFT). Total of 318 CT scans were identified as unreadable on quality checks (primarily due to missing data or motion artifact) during original study. Source.—Reference 4. Deep learning algorithm failed to produce results on 10 CT scans. Total of 1962 participants with analyzable CT were included in testing cohort. CNN-LSTM = convolutional neural network and long short-term memory.