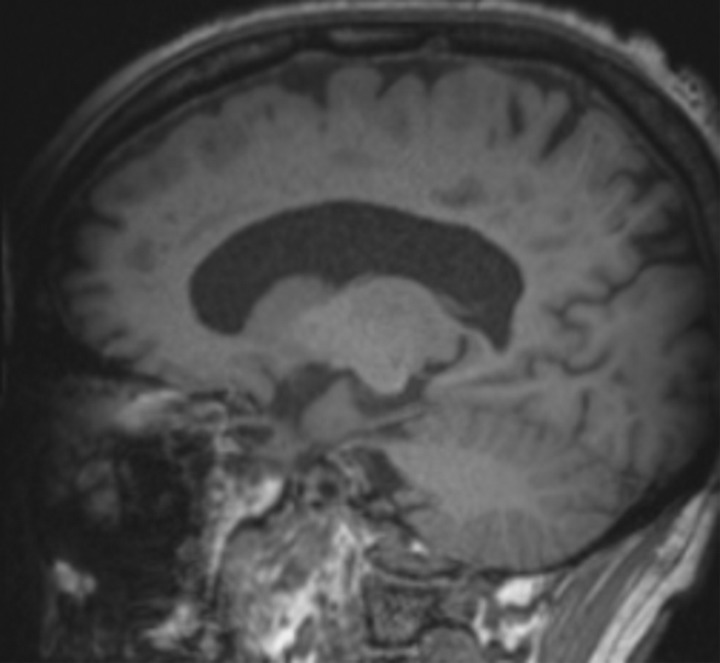
Figure 16a.
Patient with memory loss. (a) Sagittal T1-weighted MR image in a patient with memory loss shows relatively preserved cortical volume. (b) Axial 18F-florbetaben image at the level of the lateral ventricles shows diffuse abnormal uptake, confirming amyloid deposition. (c) Axial image at the level of the cerebellum shows preserved gray-white differentiation. (d, e) Axial susceptibility-weighted minimum intensity projection images at the level of the atria (d) and body (e) of the lateral ventricles show multiple areas of round signal void (arrows) scattered throughout the periphery of the cortices, compatible with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. (f) Axial susceptibility-weighted minimum intensity projection image at the level of the cerebellum shows the lack of abnormal susceptibility in the cerebellum, compatible with the sparing noted at amyloid PET imaging. This case highlights the complementary role of structural and molecular imaging with findings compatible with Alzheimer disease and cerebral amyloid angiopathy.