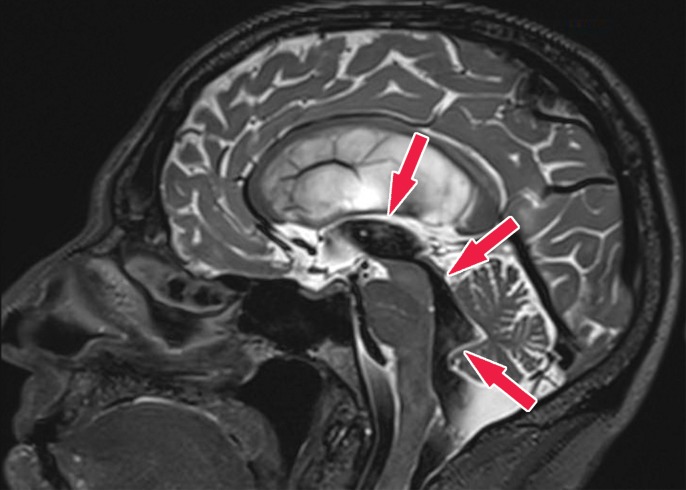
Figure 23b.
Patient with normal pressure hydrocephalus with insidious onset of dementia, gait disturbance, and urinary incontinence. Coronal T2-weighted (a) and sagittal T2-weighted three-dimensional–volumetric high-spatial-resolution (b) MR images show ventriculosulcal disproportion, which is suggestive of normal pressure hydrocephalus. Three-dimensional–volumetric high-spatial-resolution images also show a large cerebrospinal fluid flow void (arrows) at the level of the third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, and fourth ventricle, suggesting increased velocities and excluding obstruction, which helps confirm normal pressure hydrocephalus.