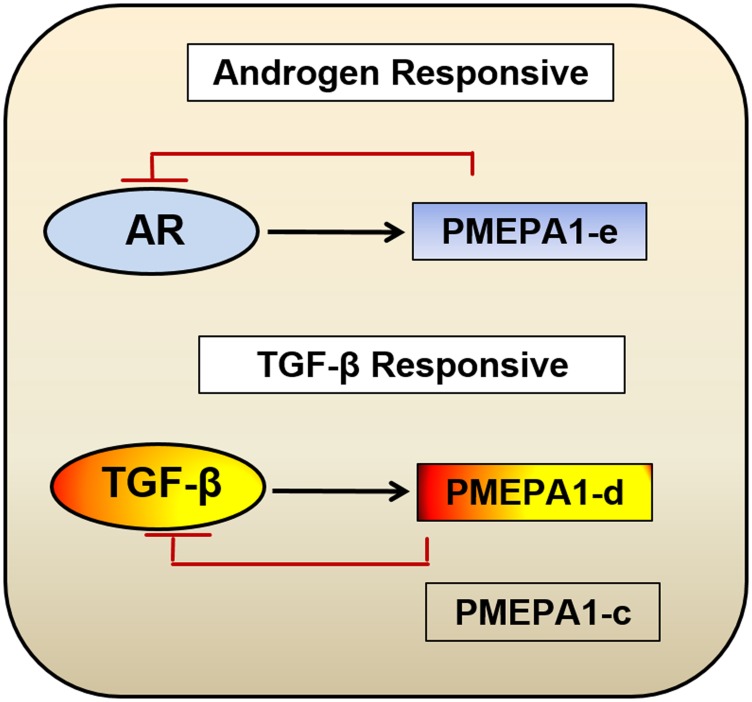
Figure 8. Model for biological function categorization of PMEPA1 isoforms (c, d and e) in the context of prostate cancer.
Our study suggested a model where evaluation of PMEPA1 isoforms revealed a potentially new mechanism of prostate cancer cell adaptation from androgen dependent to hormone independent, TGF-β controlled cell growth. PMEPA1-e were androgen responsive whereas the PMEPA1 isoform c and d were TGF-β responsive and only isoform d inhibited TGF-β signaling.