Figure 3.
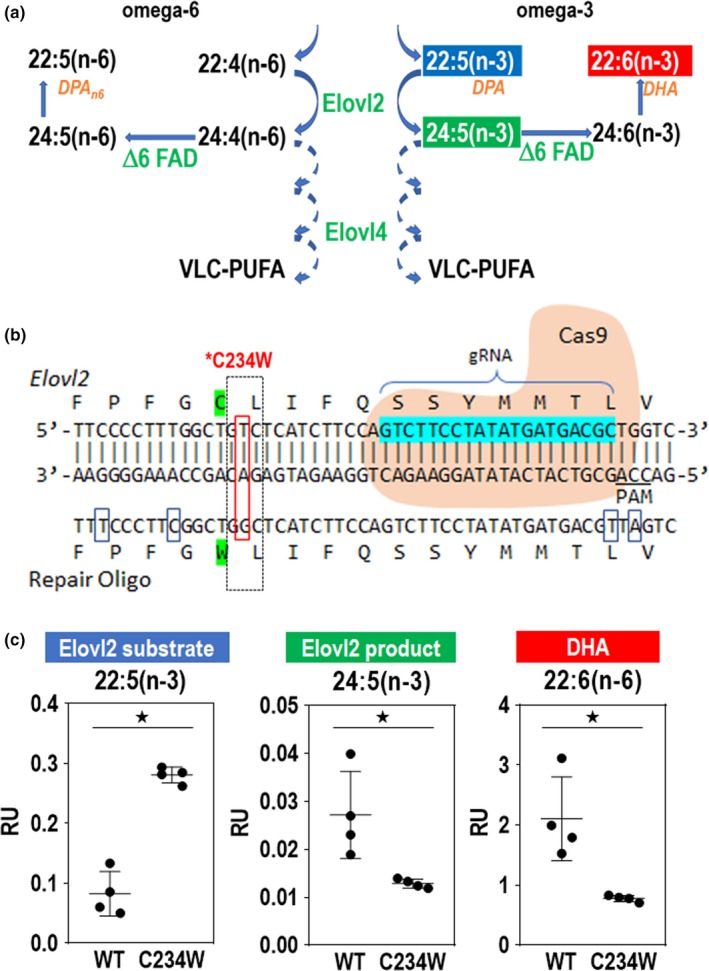
Elovl2 C234W mice show a loss of ELOVL2 enzymatic activity. (a) Schematic of ELOVL2 elongation of omega‐3 and omega‐6 fatty acids. ELOVL2 substrates 22:5 (n‐3) and 22:4(n‐6) are elongated by ELOVL2 to 24:5(n‐3) and 24:4(n‐6). This leads to other products such as DHA, DPAn6, and VLC‐PUFAs, which are elongated by ELOVL4. (b) CRISPR‐Cas9 strategy to create Elovl2 C234W mice. Elovl2 gRNA, Cas9, and repair oligo are used to create the Elovl2 C234W mutant. (c) Lipid levels of ELOVL2 substrate DPA (22:5(n‐3)), ELOVL2 product (24:5(n‐3)), and DHA (22:6(n‐3)) in retinas of Elovl2 C234W mice and wild‐type littermates. N = 4, *p < .05 by Mann–Whitney U test. Error bars represent SD
