Figure 1.
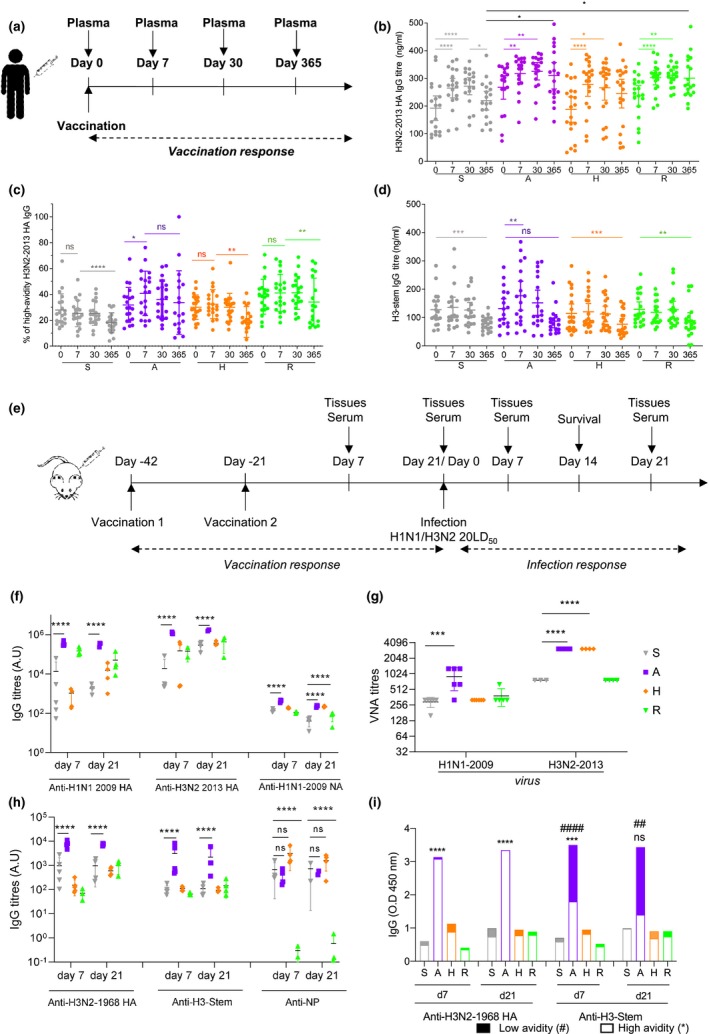
A‐eIIV induces high‐avidity H3‐2013 and H3‐stem IgG in humans and mice. A randomised clinical trial to assess eIIV immunogenicity compared with S‐IIV, sampled blood plasma at days 0 (baseline), 7, 30 and 365 after vaccination (a). H3N2‐2013 HA titres (b), high‐avidity H3N2‐2013 HA (c) and H3‐stem‐specific (d) IgG responses were measured by ELISA. The same vaccines were assessed in a mouse model of vaccination and infection (e). Vaccine strains, H1N1‐2009 and H3N2‐2013 HA‐specific and H1N1‐2009 NA‐specific, day 7 and 21 post‐vaccination IgG titres by ELISA (f) and day 21 post‐vaccination by VNA (g). Cross‐reactive, H3N2‐1968, H3‐stem HA‐specific and NP‐specific, day 7 and 21 post‐vaccination IgG responses by ELISA (h). Proportion of low‐ and high‐avidity H3N2‐1968 HA and H3‐stem‐specific IgG (i). Data represent the mean, SEM and individual responses, (b–d) n = 20 per group and (f–i) n = 4 or 5 per group. For b–d, *shows statistical significance by one‐way ANOVA with the Friedman test in each vaccine group day 0 versus days 7, 30 and 365. For (f–i), *shows statistical significance by one‐way ANOVA (mixed model) for eIIV versus S‐IIV by Tukey's multiple comparison test. For (i), #shows statistical significance for low‐avidity antibodies and *for high‐avidity antibodies for eIIV versus S‐IIV by one‐way ANOVA (mixed model) and Tukey's multiple comparison test. # or *P < 0.05, ## or **P < 0.01, ### or ***P < 0.005, #### or ****P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.005, experiments were repeated twice. Human serological experiments were performed with n = 20 individuals/group, experiments were repeated twice. Mouse experiments were performed with individual mouse serum from 4‐5 mice, and experiments were repeated twice.
