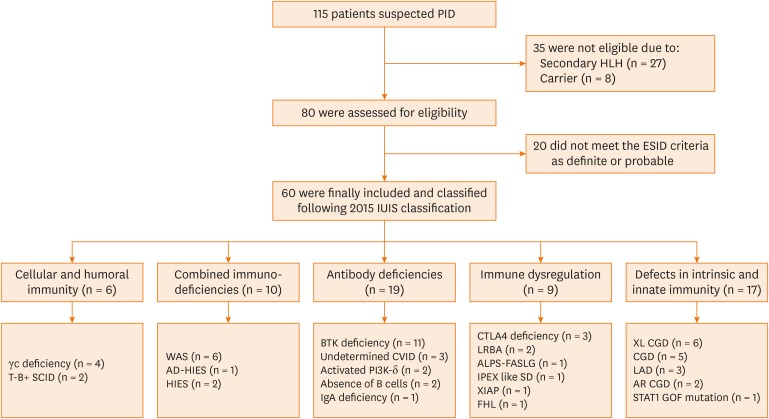
Fig. 1. Enrollment and classification of patients.
PID, primary immunodeficiency disease; HLH, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; ESID, European Society of Immune Deficiencies; IUIS, International Union of Immunological Societies; WAS, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; AD-HIES, autosomal dominant-hyper-IgE syndrome; HIES, hyper-IgE syndrome; BTK, Bruton's tyrosine kinase; CVID, common variable immune deficiency; IgA, immunoglobulin A; CTLA4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4; ALPS, autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome; AR-CGD, autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous diseases; FHL, familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; LAD, leukocyte adhesion deficiency; SCID, severe combined immunodeficiency; IPEX-like SD, immunodysregulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X-linked syndrome; XL-CGD, X-linked-chronic granulomatous diseases; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; GOF, gain-of-function.