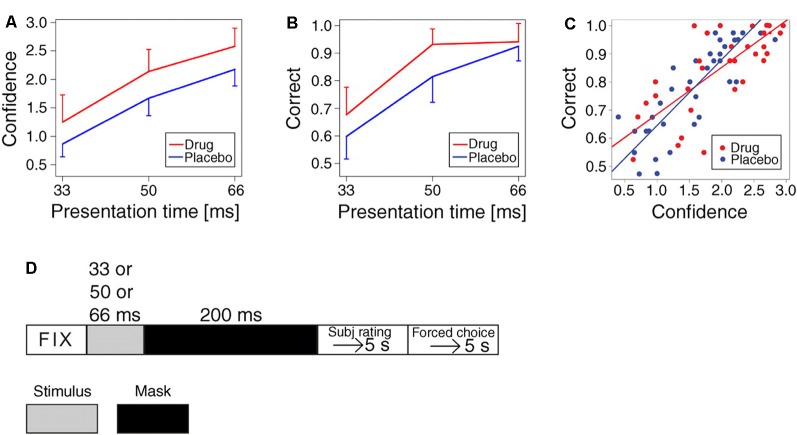
Figure 1.
Effect of dopaminergic activation on confidence in seeing words and on accuracy in word recognition task. (A) Increase in the subjective rating of confidence (scale 0–3) for words presented at 33 ms, 50 ms, and 66 ms (means and standard deviations of means, p = 0.0018). (B) Increase in accuracy (percentage of correct responses, in word recognition task by forced choice, one distractor). The expectation from chance: 50%. Note ceiling effect (p = 0.006). (C) All observations of correct answers as a function of confidence, showing a significant effect (p < 0.0001, regression with random effect). The pergolide-treated group and the placebo groups had identical regression lines statistically. (D) Experimental timeline (Lou et al., 2011, p. 3). Adapted with permission from Lou et al. (2011).