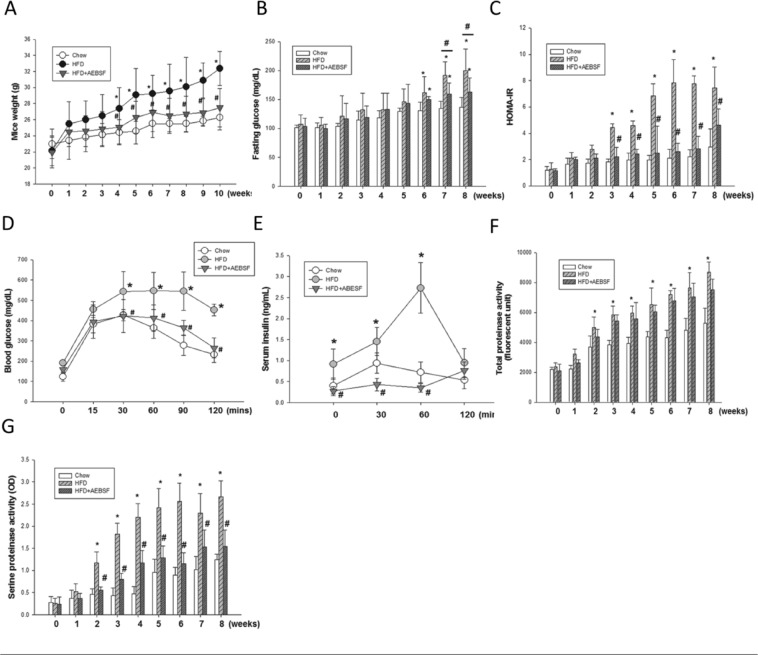
Figure 2.
4-(2-Aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride (AEBSF) attenuated high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity and insulin resistance in male LDLR−/− mice. (A) HFD-induced weight gain (n = 6–9/group). (B) Plasma concentrations of fasting glucose (B; n = 6−12/group) and Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR; C; n = 6−9/group) in mice receiving HFD and HFD + AEBSF treatments. Plasma concentrations of glucose (D) and insulin (E) in an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test for mice receiving the chow, HFD, and HFD + AEBSF treatments (n = 6/group). Total (F) and serine (G) protease activities in mice receiving the chow, HFD, and HFD + AEBSF treatments (n = 6/group) *P < 0.05, chow vs. HFD; ♯p < 0.05, HFD vs. HFD + AEBSF. Values are means ± standard deviations.