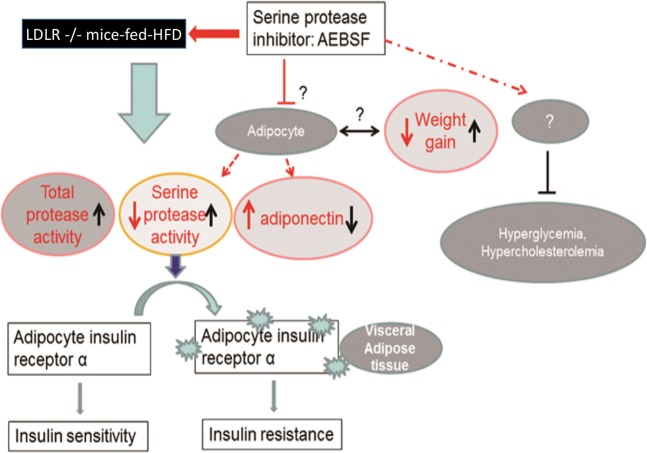
Figure 4.
Schematic overview of the contributions of serine protease to insulin resistance and obesity in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed LDLR−/− mice. These mice showed increased plasma total and serine protease activities, weight gain, and attenuated accumulation of insulin receptor-α in visceral fat tissue. Serine protease destroyed insulin receptor-α, contributing to insulin resistance. 4-(2-Aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride (AEBSF) reversed insulin resistance and weight gain. However, the detailed mechanism of the weight gain reversal, adiponectin revision, and cholesterol and blood glucose lowering effects remains unclear.