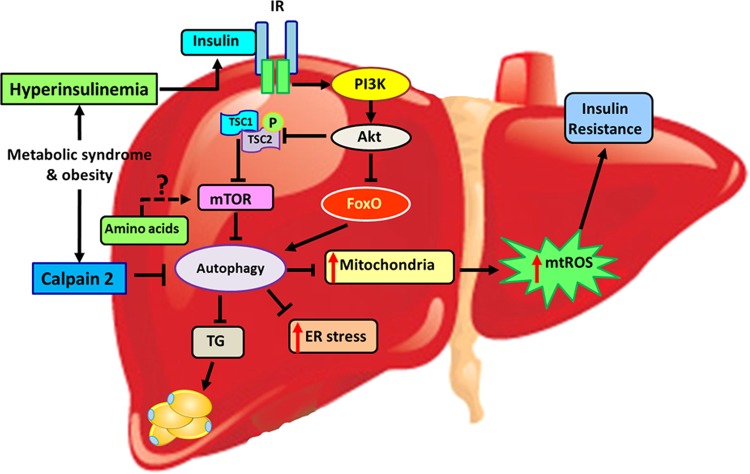
Fig. 5. The role of autophagy in the liver during metabolic syndrome.
Autophagic activity is significantly reduced in hepatocytes during obesity. Inhibition of autophagy promotes hepatocyte lipid accumulation, malfunction of mitochondria, and cell stresses including ER stress. This, in turn, induces insulin resistance, results in a fatty liver and disrupts the normal liver functions. Induced insulin secretion due to metabolic syndrome will directly affect the autophagy process by activating mTOR and inhibiting the FoxO via PI3K/Akt pathway. Moreover, increased calpain 2 will further inhibit autophagy and increase amino acid concentrations which may contribute to upregulation of mTOR activity during obesity and metabolic syndrome.