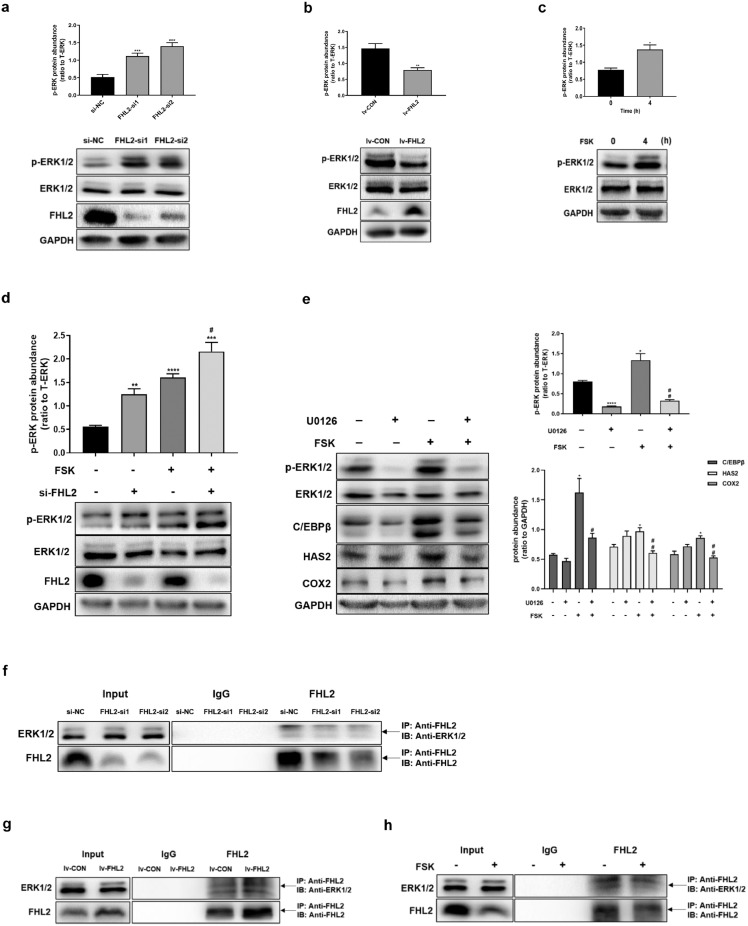
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of ERK1/2 phosphorylation by FHL2 interacting with ERK1/2 and the role of ERK signalling in regulating ovulation-related genes in KGN cells. (a) Effect of siRNA-mediated FHL2 knockdown on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2. (b) Effect of FHL2 overexpression on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2. (c) Induction on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 by FSK (10 μM, 4 h). (d) Effect of FSK (10 μM, 4 h) on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 with or without FHL2 knockdown in KGN cells. (e) Effects of FSK (10 μM, 4 h) on ERK1/2 phosphorylation, C/EBPβ, HAS2 and COX2, in the presence and absence of inhibitor for ERK1/2 (U0126, 10 μM). (f-h) The FHL2-ERK1/2 interaction was examined in KGN cells by immunoprecipitation of FHL2 from whole-cell lysates followed by immunoblotting for ERK1/2 and FHL2. FHL2-ERK1/2 interaction was detected after siRNA-mediated FHL2 knockdown (f), stable transfection mediated by FHL2 lentivirus or control vectors (g), and treatment with FSK (10 μM, 4 h) (h), respectively. Representative blots are shown and the data are means ± SEM from 3 to 5 experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. controls; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. FSK.