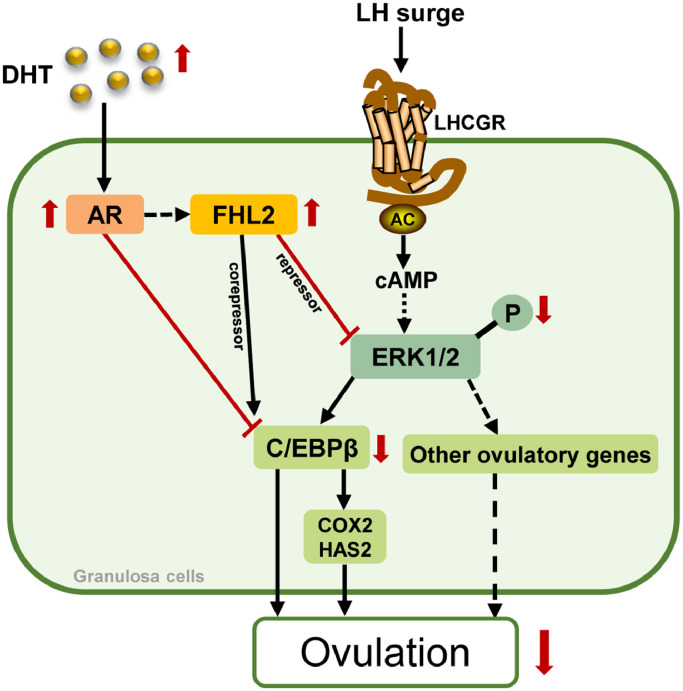
Fig. 8.
Modelling the roles of FHL2 in inhibiting ovulation in PCOS.
All of the events of ovulation are triggered by LH surge that result in the activation of LHCGR–adenylyl cyclase (AC)–cAMP in GCs. Activation of cAMP in GCs leading to activation of ERK1/2 cascade involved in oocyte maturation, cumulus expansion and follicle rupture. In PCOS, elevated FHL2 expression leads to blockade of ovulation by: (i) interacting with AR to act as its co-repressor to inhibit C/EBPβ expression; (ii) binding to ERK1/2 to inhibit its phosphorylation, inducing further suppression of C/EBPβ and other ovulatory genes. Moreover, androgen (DHT)-induced upregulation of FHL2 is mediated by AR.