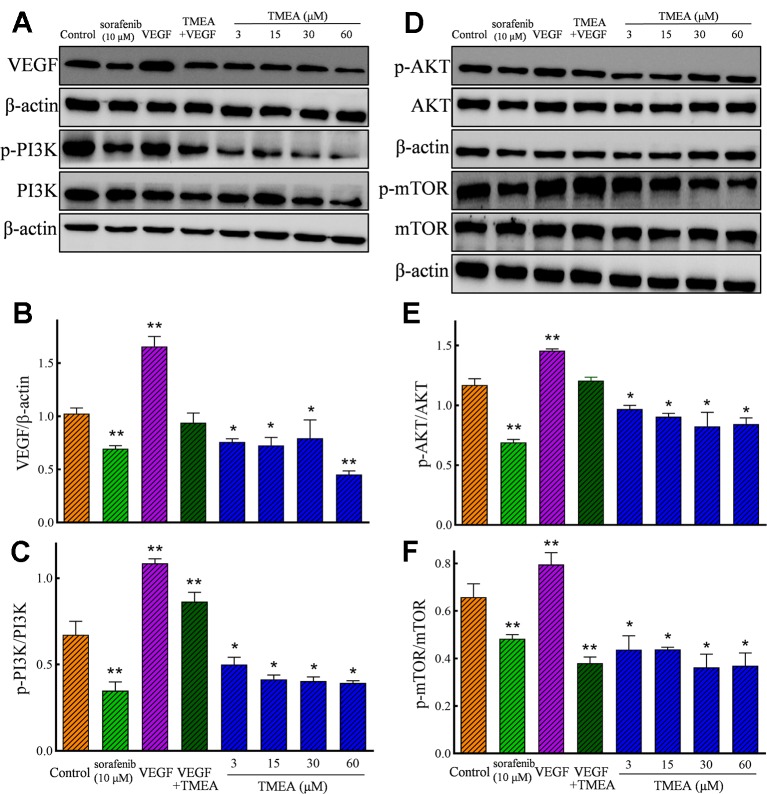
Figure 8.
Effect of TMEA on the protein expression and phosphorylation of VEGF downstream signaling molecules, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (AKT) kinase, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in HUVECs by Western blotting analysis. (A) The bands of VEGF, PI3K, p-PI3K by Western blotting analysis. (B) Summary bar graph of VEGF and (C) PI3K, p-PI3K. (D) The bands of AKT, p-AKT, mTOR and p-mTOR by Western blotting analysis; (E) Summary bar graph of AKT, p-AKT, and (F) mTOR, p-mTOR. The cells were treated with vehicle solution (control), or sorafenib (10 μM) or various concentrations of TMEA (3, 15, 30, and 60 μM) for 12 h. β-actin was used as an internal control. The data are presented from at least three independent experiments run in triplicate and expressed as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared with the vehicle-treated controls by one-way univariate analysis of variance. TMEA, 3,3',4'-trimethylellagic acid; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.